Not long ago, a product team we worked with spent two full days trying to understand why half of their automated regression suite suddenly failed. Nothing in the codebase had changed and no deployments had gone out. Turns out, a small, unannounced update to a shared UI component quietly broke multiple points across their automation testing pipeline. Two days of debugging to discover nothing was actually wrong with the product — only the tests.
Stories like this have become increasingly common. As release cycles accelerate and systems grow more interconnected, teams find themselves maintaining automation more than they maintain the software it’s supposed to protect.
This is where autonomous testing comes in. By using intelligent systems that adapt, learn, and respond to change during the testing process, teams finally gain a way to keep quality aligned with modern delivery speeds, without drowning in brittle scripts and maintenance overhead.
Key Takeaways
- Autonomous testing is an approach that uses AI-driven logic to adapt tests during execution and reduce maintenance.
- Autonomous QA differs from automation testing by making independent decisions, not just running scripts.
- Autonomous testing improves stability by self-healing locators and flows in real time.
- It increases meaningful test coverage through exploration and risk-based prioritization.
- Autonomous tools react to UI, API, and data changes faster than scripted automation.
- Autonomous testing fits naturally into CI/CD pipelines and fast-moving engineering teams.
- Intelligent testing reduces false positives and accelerates debugging across environments.
- Human QAs remain essential for risk analysis, oversight, and exploratory testing.
- Autonomous QA can have a positive impact on any industry, but platforms in fintech, healthcare, SaaS, and logistics benefit especially greatly from autonomy.
- Autonomous testing evolves continuously, shaping future testing strategies and quality practices.
What Is Autonomous Testing and How It’s Different From Traditional Automation Testing
Autonomous testing is an emerging discipline that applies advanced AI and machine reasoning to software testing without human intervention. In practice, this means a system can generate tests, navigate applications, make decisions during test execution, and update itself as requirements evolve.
Where traditional automation testing depends on predefined scripts, autonomous software testing uses adaptive logic, learning mechanisms, and semantic understanding. This shift makes autonomous testing a modern approach to software testing — one that is capable of keeping up with today’s rapid release cycles and increasingly complex architectures.
Basic definition
Autonomous testing is a testing approach where the majority of testing decisions — what to test, how to test, and how to maintain tests — are performed by an intelligent system using AI models, reasoning capabilities, and behavioral data.
What makes it different from traditional test automation
Autonomous testing is a modern approach because it moves from executing what humans created to creating and adapting tests on its own. It does not remove human testers; it shifts their role into oversight, risk evaluation, and boundary-setting.
Key characteristics of autonomous testing include:
- AI-driven decision-making. The system determines test flows, adapts to changes, and updates tests automatically. This is where autonomous testing employs artificial intelligence and testing uses AI and machine learning.
- Self-healing behavior. Tests fix broken selectors or alternative paths without human intervention.
- Contextual awareness. The tool analyzes logs, user journeys, and system behavior to choose what to validate.
- Continuous learning. Models used in autonomous testing improve over time based on production signals and historical failures.
- Scalable execution. Supports large test suites without demanding proportional test maintenance.
Together, these capabilities allow autonomous testing to function as a next-generation layer on top of traditional test automation, filling the gaps that scripted automation cannot handle.
We’ll combine automation, AI, and autonomous testing to build a QA strategy that meets your needs.
Manual testing vs. automation testing vs. autonomous testing
Before we dive into the detailed comparison, it’s useful to understand the mindset and operational differences between these three approaches. Although they all belong to the broader testing process, they serve fundamentally different purposes in the testing lifecycle and rely on different levels of human involvement, adaptability, and intelligence.
Manual testing is rooted in human judgment. Testers explore the application, interpret behavior, and make decisions based on expertise, domain knowledge, and intuition. It excels at uncovering usability issues, ambiguous requirements, and unexpected edge cases — the kinds of insights that require human creativity and reasoning. But because every action is executed manually, scalability is limited, and repetitive tasks quickly become costly and time-consuming.
Automation testing, on the other hand, focuses on speed and repeatability. It allows teams to automate test steps for stable, predictable flows, especially for regression or repetitive tasks. However, automation relies on scripts and rules written by humans. If the UI changes, an API evolves, or the flow shifts, those scripts break. Maintaining them becomes a significant part of the testing workload, and the system can only perform what it is explicitly told to do.
Finally, autonomous testing introduces a fundamentally different model. Instead of executing human-written scripts, an autonomous testing system uses AI-driven logic to make decisions during test execution, adapt to changes, explore new paths, and even update or generate tests on its own. While humans define boundaries, goals, risks, and constraints, the system performs the majority of operational work. It doesn’t just run tests — it interprets behavior, learns from failures, and improves test coverage dynamically.
In other words:
- Manual testing is human-driven discovery.
- Automation testing is script-driven execution.
- Autonomous testing is AI-driven decision-making and adaptation.
Let’s take a closer look at the key differences between the three subsections of testing in the table below.
| Aspect | Manual testing | Automation testing | Autonomous testing |
| Definition | Human testers execute all steps manually | Scripts automate repeatable tasks | AI-driven system performs software testing without human intervention |
| Who makes decisions | Humans | Humans write & maintain scripts | Autonomous testing system makes the majority of testing decisions |
| Test creation | Manual | Scripted | Generated or adapted using AI models |
| Maintenance | Human-driven | Requires regular updates | Self-healing; autonomous software testing uses contextual modeling |
| Adaptability | Low | Medium | High — autonomous testing uses AI to re-evaluate UI and API behavior |
| Scalability | Limited | Dependent on infrastructure | Infrastructure + intelligence driven |
| AI use | None | Optional | Core capability; testing uses AI and machine learning |
| Strengths | Creativity, domain insight | Repeatability, speed | Adaptability, resilience, continuous validation |
Why autonomous testing is currently emerging
Autonomous testing is an emerging solution because modern software environments outgrow the capabilities of manual or scripted automation. Systems today are:
- highly distributed
- API-driven
- constantly changing
- influenced by real-time data
- integrated through dozens of services
This creates testing needs that cannot be covered with traditional automation tools alone.
1. Software complexity has exceeded human-maintainable test automation
Teams now work with:
- microservices
- asynchronous events
- dynamic UIs
- multi-step authentication
- AI-powered features
- evolving user flows
Each change can break dozens of tests. Script maintenance becomes unsustainable.
Autonomous testing employs AI to:
- detect UI/API shifts
- choose new test paths
- repair failing flows
- propose updated assertions
- re-evaluate system behavior without supervision
2. Release cycles demand continuous, intelligent quality signals
Modern delivery practices — CI/CD, trunk-based development, and feature flags — require:
- real-time validation
- adaptive test execution
- risk-based test selection
- rapid interpretation of failures
Traditional automation testing cannot respond intelligently to change. Autonomous testing, in turn, uses AI models to adjust at runtime, making the testing process more resilient.
3. Advances in AI make autonomy finally possible
The rise of:
- LLMs
- reinforcement learning
- behavior modeling
- multi-agent reasoning
- production telemetry analytics
has enabled models used in autonomous testing to interpret UIs, API schemes, and user journeys in a more human-like (yet scalable) way.
These developments support:
- element recognition beyond selectors
- context-aware decision-making
- dynamic exploration of unknown flows
- realistic and diverse test data generation
4. The cost of test maintenance is becoming unacceptable
Organizations lose enormous time and budget to:
- fixing fragile scripts
- re-running regressions manually
- updating assertions after every redesign
- debugging false failures
Autonomous testing reduces this burden by shifting maintenance to the autonomous testing system, which can update itself based on application behavior.
5. AI adoption in engineering creates expectations in QA
As AI optimizes development, operations, monitoring, and security, stakeholders naturally expect:
- smarter testing
- fewer manual steps
- faster decision-making
- higher-quality insights
This is why autonomous testing is still evolving but rapidly gaining traction as the modern approach to software testing.
Get more from your testing process with our QA consulting expertise.
What Can You Do With Autonomous Software Testing?
Autonomous software testing offers far more than simply running automated scripts faster. It introduces capabilities that extend across the entire testing lifecycle, supporting complex decision-making, adaptive maintenance, and intelligent exploration of systems. Instead of relying on brittle scripted flows, autonomous testing uses AI models and behavior analysis to expand test coverage, discover risks, and improve test reliability with minimal manual intervention.
Below are the core areas where autonomous testing provides practical, high-impact value.

1. Generate and maintain tests automatically
One of the most transformative capabilities is the ability to create and update tests without human scripting. This includes:
- generating initial test flows by exploring the application
- identifying new or modified elements dynamically
- repairing broken selectors through AI-driven test adaptation
- updating assertions based on behavioral changes
- supplementing missing coverage with new suggested scenarios
This directly reduces manual maintenance, which is one of the biggest bottlenecks in traditional automation tools, as well as supports both speed and accuracy in the testing process.
2. Navigate complex test scenarios intelligently
Traditional automation executes predetermined steps. Autonomous testing, however, can adapt at runtime and reason about new or unfamiliar states.
This includes:
- resolving unexpected popups or interstitial screens
- exploring branching paths triggered by user inputs or roles
- identifying risky flows based on system behavior
- validating multi-step or multi-service interactions
For distributed systems, microservices, or dynamic UIs, this adaptability becomes essential. It allows teams to validate complex test scenarios without writing endless conditional logic.
3. Detect changes and self-heal test flows
Autonomous testing employs AI to detect changes across interfaces, APIs, and data structures, allowing it to:
- identify updated UI elements even if selectors change
- detect modified API schemes and adapt accordingly
- re-route flows when expected steps are missing
- update locators, parameters, or inputs without human involvement
This prevents regressions from breaking entire suites and keeps ongoing test execution stable across releases.
4. Prioritize tests based on real risk
Instead of running everything blindly, an autonomous testing tool can use:
- application logs
- observability data
- usage analytics
- historical failures
- code changes
- test impact analysis
to decide what should be tested first.
This risk-based prioritization ensures the system focuses on the highest-value testing activities, especially under tight delivery timelines.
5. Expand test coverage beyond scripted boundaries
Because autonomous testing uses reasoning and exploration, it can discover:
- hidden paths
- incomplete journeys
- under-tested logic branches
- overlooked integration points
- stale assumptions in existing automation
This allows the system to propose additional scenarios and uncover gaps that traditional automation testing cannot reach.
It effectively upgrades teams from “we automated the most obvious flows” to “we continuously discover and validate the real behavior of the system.”
6. Support continuous testing across environments
Autonomous testing integrates naturally with continuous testing, CI/CD pipelines, and production monitoring, enabling it to:
- run tests triggered by code changes
- validate new builds automatically
- react to real-time production signals
- analyze failures without human triage
- maintain availability of fresh quality insights throughout the day
Instead of periodic regressions, teams gain a continuous testing approach aligned with modern DevOps practices.
7. Validate APIs, data flows, and backend logic
While many people think of autonomous testing as UI-focused, advanced systems can:
- discover undocumented API endpoints
- infer expected request/response patterns
- test data transformations
- detect drift
- validate message queues, event streams, or webhook flows
This broadens test coverage across layers that traditional UI-only automation often misses.
8. Create realistic and diverse test data
AI-based generators help satisfy testing needs for:
- edge cases
- rare combinations
- localization scenarios
- negative tests
- performance-sensitive inputs
- data variations across user types
This results in more reliable testing, especially for products with complex logic or compliance constraints.
9. Adapt testing to evolving product needs
Autonomous testing supports long-term agility because it:
- updates itself as the product changes
- adapts to modern UI frameworks
- understands component logic
- reacts to API evolutions
- learns from real-world failures
This ensures the testing system is not static but evolves alongside the software it protects.
10. Reduce manual management and noise
AI-based analysis helps identify:
- flaky tests
- root-cause clusters
- failure correlations
- false positives vs. genuine defects
This reduces operational noise and removes one of the hardest parts of traditional automation testing: figuring out why something failed.
Key Benefits of Autonomous Testing
The benefits of autonomous software testing solutions extend far beyond simple efficiency improvements. While traditional automation testing provides speed and consistency, it still relies on humans to write scripts, maintain flows, and interpret failures. Autonomous testing, by contrast, introduces a level of intelligence and adaptability that allows the testing process to evolve continuously, improving accuracy, resilience, and long-term scalability.
Here are the core benefits of autonomous testing that teams experience when they integrate autonomous systems into their quality strategy.
1. Dramatically reduced maintenance effort
One of the biggest challenges in automation is the constant upkeep of test scripts. Small UI changes, new fields, updated flows, or API adjustments can break dozens of tests at once.
Autonomous testing addresses this through:
- automatic locator repair and self-healing
- dynamic adaptation to UI or API changes
- runtime decision-making for unexpected states
- continuous refinement of existing flows
This not only stabilizes test execution but also frees QA engineers to focus on strategy, exploratory work, and higher-value testing activities rather than firefighting broken scripts.
2. Higher and more meaningful test coverage
Traditional automation often covers only predictable, stable paths. Autonomous testing expands test coverage by:
- exploring untested areas of the application
- discovering alternative flows based on user behavior
- identifying integration points that manual scripts might miss
- generating additional scenarios where risk is high
Because autonomous testing uses AI to analyze behavior, logs, and historical failures, it continuously identifies gaps and proposes new ways to improve test relevance and completeness.
3. Faster detection of regressions and critical issues
Autonomous testing can operate continuously across environments, making it ideal for CI/CD pipelines and rapid iteration. Teams can benefit from:
- instant test execution after every code change
- automated prioritization of high-risk tests
- near-real-time detection of regressions
- early discovery of failures before they reach production
This “always-on” quality layer supports a far more efficient testing lifecycle, reducing defect escape rates and shortening the time between discovery and resolution.
4. Adaptability to change across UI, API, and backend layers
Modern systems change constantly. Feature flags toggle new interfaces, APIs are refactored, and microservices shift behavior. Autonomous testing adapts to this complexity by:
- analyzing changes in structure or behavior
- updating flows automatically
- adjusting for new states or alternate paths
- maintaining resilience across integrations
Where traditional automation tools break under change, an autonomous testing platform remains stable and reliable.
5. Better decision-making through AI-driven insights
With so much business success riding on the efficiency of testing, there is no place for guesswork when it comes to making executive decisions. Autonomous testing uses AI-driven test intelligence to:
- highlight flaky areas
- classify failures
- group defects by behavior
- identify patterns in system instability
- recommend where additional testing is needed
This reduces the cognitive load on engineering teams and creates a more informed approach to software testing. Instead of checking thousands of logs manually, QAs receive structured insights that accelerate debugging and management.
6. Improved performance validation and system reliability
Because autonomous testing can continuously observe system behavior and learn from production data, it becomes valuable not only for functional checks but also for early performance testing signals.
Examples of this include:
- detecting slowdowns in newly introduced flows
- identifying bottlenecks across microservices
- analyzing how the system behaves under certain data conditions
- recognizing degradation earlier than traditional monitoring
This hybrid visibility — functional + performance — helps organizations maintain stable and scalable systems.
7. Lower long-term cost and higher scalability
The scalability of autonomous testing comes from reducing the work humans must perform manually:
- fewer hours spent fixing automation
- fewer repetitive regression runs
- fewer false failures
- fewer manual confirmations
- more predictable testing cycles
As the system learns, the cost of maintaining quality decreases, even as product complexity grows. This makes autonomous testing a powerful strategy for teams aiming to scale testing without scaling headcount.
8. Enhanced reliability for AI-driven applications
Because today’s products increasingly incorporate AI-driven test logic, decision systems, LLM-based features, and personalized flows, traditional scripted tests often fail to capture their variability.
Autonomous testing is uniquely suited for this because it:
- adapts to dynamic responses
- navigates unpredictable user paths
- learns from behavioral patterns
- validates complex interactions that rule-based scripts cannot anticipate
This positions autonomous testing as essential for modern intelligent applications.
Give your software a quality boost with expert QA services.
Where Autonomous Testing Fits in the Modern SDLC and DevOps Ecosystem
Autonomous testing enhances — not replaces — the existing testing lifecycle. It integrates with the same environments, processes, and quality engineering workflows used for test automation today, but it introduces intelligent decision-making and continuous adaptation. This makes it a natural fit for modern delivery models built around CI/CD, microservices, and rapid iteration.
Unlike traditional automation testing, which relies on predefined scripts, autonomous testing adapts its behavior using AI-driven reasoning. This allows it to provide continuous quality feedback throughout the entire SDLC, from development and integration to staging, pre-production, and even production monitoring.
Here are the primary stages in the lifecycle where integrating autonomous testing delivers measurable value.
1. During development: instant feedback at the code and feature level
At the earliest stages of development, autonomous testing can work alongside developers to provide continuous signals through:
- on-commit validations
- intelligent test execution prioritization
- adaptive checks triggered by specific code changes
- risk-based selection of relevant tests
- detection of unstable or breaking UI/API elements
This complements unit tests and traditional automation tools, improving speed and reducing the feedback delay that often slows engineering teams.
2. During integration: validating interactions across services and interfaces
In modern architectures, integration points change frequently. Autonomous testing observes these patterns and dynamically adjusts tests based on:
- updated API schemes
- modified message flows
- changed dependencies
- new or deprecated endpoints
Because autonomous testing can interpret application structure, it automatically selects the right testing approach for each integration point, reducing the manual effort needed to maintain complex integration suites.
3. In staging: risk-based testing with live-like data
Staging environments are where teams typically evaluate whether the system behaves correctly end-to-end. Autonomous testing enhances this step by:
- generating exploratory flows
- comparing behavior against historical patterns
- running testing activities with realistic and diverse test data
- monitoring functional and early non-functional trends
- identifying areas lacking sufficient test coverage
This hybrid of risk analysis and autonomous exploration is difficult to achieve with scripted test automation alone.
4. In pre-production: validating release candidates dynamically
Before a release, engineering teams need confidence that the application works across multiple configurations, roles, and data scenarios. Autonomous testing:
- executes high-value flows across different versions
- adapts to changes introduced by feature flags
- detects regressions not caught by static automated suites
- identifies performance or stability issues emerging from fresh builds
This makes it highly effective for release gating, where speed and reliability are equally important.
5. In CI/CD pipelines: continuous, intelligent quality signals
As deployments become more frequent, reliable automation becomes essential. Autonomous testing supports CI/CD by:
- reacting to events, not time-based schedules
- using dynamic prioritization rather than running all tests
- supporting high-throughput development environments
- performing continuous validation even when changes are small
Because autonomous testing learns from code diffs, historical defects, and behavior patterns, it turns CI pipelines into a smarter, context-aware quality layer.
6. In production and monitoring systems: closing the feedback loop
Modern testing needs do not end at deployment. With the right safeguards, autonomous testing can use production data to improve quality by:
- identifying real user flows not covered by scripted tests
- informing decisions about future test generation
- detecting silent failures and intermittent functional issues
- correlating telemetry patterns with test relevance
- refining subsequent test cycles for higher accuracy
This feedback-driven evolution allows the testing platform to stay aligned with real-world behavior instead of drifting over time.
7. Enhancing team collaboration across QA, Dev, and Ops
Because autonomous testing produces insights — not just pass/fail results — it becomes a shared intelligence layer across multiple teams:
- Developers get fast, actionable feedback
- QA engineers get reduced maintenance work and richer insights
- DevOps teams get stability signals aligned with runtime behavior
- Product owners gain visibility into system health and risk
The result is a more unified engineering culture with fewer roadblocks and clearer quality ownership.
How to Implement Autonomous Testing: A Practical Maturity Model
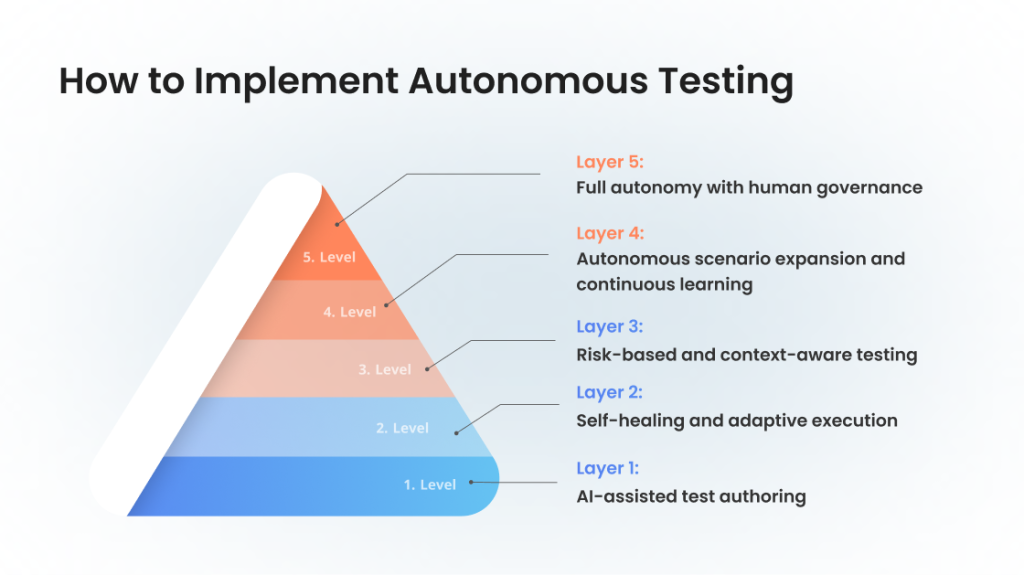
Implementing autonomous testing is not something teams do overnight. It’s a progressive expansion of capabilities, starting with AI-assisted scripting and moving toward systems that adapt, reason, and participate in quality decisions.
A maturity-based approach helps organizations introduce autonomy into their testing process without disrupting existing workflows or overwhelming their teams.
Here is a streamlined, practical autonomous software testing model consisting of five levels. Each stage adds a layer of intelligence, reduces maintenance, and brings teams closer to fully adaptive, AI-driven quality practices.
Level 1: AI-assisted test authoring
Most organizations begin here. Testing still relies on traditional test automation, but AI is introduced to accelerate repetitive work. Testers can describe flows in natural language, get suggestions for assertions, and generate script templates faster than before.
At this stage, the autonomous testing tool you choose does not make decisions on its own; it simply supports humans in creating artifacts more efficiently. The value lies in reducing the friction of early scripting and helping teams establish stable coverage without increasing workload.
This level is ideal for teams who want to introduce intelligence gradually while keeping their existing automation tools and frameworks.
Level 2: Self-healing and adaptive execution
Here, autonomy becomes visible. During test execution, the system detects when UI elements, API responses, or workflows change and adapts in real time. Instead of failing instantly, tests repair their locators, re-evaluate paths, or adjust to updated structures. This reduces the maintenance burden dramatically, especially for fast-moving teams where even small UI adjustments can break dozens of scripts.
At this level, the autonomous testing system focuses on stability: it ensures that automation doesn’t degrade simply because the product evolves. Testers move from fixing brittle scripts to validating the decisions the system makes.
Level 3: Risk-based and context-aware testing
As organizations expand autonomy, the system begins to influence what gets tested and when. This moves beyond execution into strategic, context-aware decision-making. Instead of blindly running full regression suites, autonomous testing uses signals from code changes, production behavior, analytics, and historical failures to prioritize relevant scenarios. It may recommend areas with low test coverage, highlight patterns associated with instability, or propose entirely new tests where risk is rising.
At this stage, teams experience substantial acceleration: pipelines run faster, failures are more meaningful, and the testing lifecycle becomes more intelligent.
Level 4: Autonomous scenario expansion and continuous learning
With a solid foundation in risk-based execution, the system can now begin expanding the testing scope independently. It interprets the structure of the application, explores previously untested flows, and generates new scenarios in response to changing behaviors.
This is where autonomous software testing moves beyond maintaining existing tests and begins shaping the suite itself. Over time, the system learns from patterns — both failures and successes — and redesigns parts of the suite to match evolving testing needs. Testers guide this evolution rather than manually rewriting tests.
At this level, the blend of reasoning, exploration, and adaptation forms the core intelligence of the solution.
Level 5: Full autonomy with human governance
The highest level of maturity doesn’t mean removing humans; it means shifting humans into supervisory and strategic roles.
At this point, the system participates in the entire testing approach: planning, selection, maintenance, exploration, and cross-environment validation. It identifies new risks, evaluates product behavior, correlates signals from multiple sources, and executes the most relevant tests autonomously. Teams set guardrails and approve boundaries. The system handles operational work.
This is what implementing and maintaining autonomous testing ultimately looks like: continuous, intelligent adaptation driven by AI, governed by humans, and aligned with real-world product behavior.
Autonomous Testing vs. Testing AI Systems: Why They Are Distinctly Different
Although the two concepts sound similar, autonomous testing and testing AI systems solve fundamentally different problems. Many teams use the terms interchangeably, but doing so leads to unclear expectations, mismatched test strategies, and unreliable results. Understanding the difference is critical because each discipline requires its own tools, skills, and evaluation methods within the broader testing process.
What is autonomous testing?
Autonomous testing refers to a testing approach where the system uses AI-driven logic to support or replace human decisions during test execution. It focuses on how testing is performed.
Key characteristics include:
- self-healing tests
- adaptive navigation through applications
- automated test generation and prioritization
- continuous learning from system behavior
Here, AI assists or leads the work traditionally done by humans or scripted test automation. The goal is to reduce maintenance, expand coverage, and keep the testing lifecycle aligned with rapid product changes.
What is testing AI systems?
Testing AI systems focuses on validating how AI models behave under different conditions. It evaluates whether the model:
- produces accurate and consistent responses
- avoids harmful, biased, or risky outputs
- handles ambiguous inputs safely
- behaves reliably over time
This type of testing requires specialized evaluation methods, golden datasets, and scenario design that anticipates unpredictable behavior.
The goal is not to automate tests but to understand whether the AI-driven test subject itself behaves correctly.
How are they different?
Let’s break down the key differences between the two with a quick comparison.
| Aspect | AI testing | Autonomous testing |
| Focus | How tests are executed and maintained | How an AI model behaves |
| Goal | Reduce effort, increase stability & coverage | Ensure accuracy, safety, and reliability |
| Primary techniques | Exploration, self-healing, adaptive flows | Benchmarking, scenario validation, data evaluation |
| Object of testing | Applications, APIs, journeys, integrations | AI models, prompts, model outputs |
| Human role | Supervision and review | Designing evaluation criteria & datasets |
In short, both disciplines complement each other, but they must be treated separately to ensure reliable results.
Testing an AI system? We are here to help.
Metrics and KPIs to Evaluate the Success of Autonomous Testing
To measure whether autonomous testing is delivering meaningful value, teams need metrics that go beyond simple pass/fail counts. Because an autonomous testing system makes decisions, adapts tests, and influences the testing process, its success must be evaluated through stability, coverage, efficiency, and long-term impact on the testing lifecycle.
Here are the most important KPIs for assessing performance and ensuring that autonomous testing continues to improve test reliability at scale.
- Reduction in maintenance effort. Measures how much time teams save by avoiding locator repairs, script updates, and repetitive fixes.
- Stability of test execution. Tracks decreases in flaky tests, false positives, and recurring instability across environments.
- Risk-based coverage improvement. Evaluates whether the system expands test coverage in high-risk or previously untested areas.
- Speed of feedback in pipelines. Measures how autonomy affects CI/CD performance: faster testing, more relevant prioritization, and fewer bottlenecks.
- Accuracy of autonomous decisions. Assesses how often the system’s path corrections, element identifications, or scenario choices are correct.
- Detection of regressions and anomalies. Tracks how efficiently the system identifies behavioral changes, API drift, or UI regressions compared to scripted test automation.
- Quality of generated scenarios. Reviews whether new tests created by autonomous logic increase relevance, depth, or resilience.
- Alignment with real user behavior. Measures how effectively generated tests reflect real-world flows based on telemetry or analytics.
- Coverage of integration and backend logic. Ensures the autonomous solution validates APIs, data flows, and complex interactions, not only UI steps.
- Cost-effectiveness and efficiency. Quantifies ROI through decreased manual effort, reduced pipeline time, and fewer failures that reach production.
Challenges of Autonomous Testing and How to Overcome Them
Even with significant advantages, autonomous testing introduces new complexities that teams must understand to adopt it safely and effectively. Below are the key challenges of autonomous testing and what they mean for the efficiency of the entire process.
1. Managing unpredictable AI-driven behavior
Autonomous testing uses AI to make decisions during test execution, which can introduce variability or unexpected actions. Ensuring consistency requires guardrails, controlled environments, and regular review of autonomous decisions to keep the testing process stable and aligned with product intent.
2. Ensuring test accuracy and avoiding false confidence
Because autonomy expands test coverage automatically, teams risk assuming all important flows are validated. Regular audits, clear risk models, and human oversight help maintain quality and prevent overreliance on AI-driven test generation or adaptive corrections.
3. Handling data quality and privacy constraints
Autonomous testing often relies on production-like data to identify patterns, which raises compliance and security concerns. Implementing masking, synthetic data generation, and strict access policies ensures autonomy strengthens the testing lifecycle without violating privacy or governance requirements.
4. Integrating autonomous testing tools into existing workflows
Adopting autonomy can require changes to pipelines, environments, and reporting systems. Teams may struggle fitting new capabilities into established CI/CD flows. Gradual integration, clear role definitions, and starting with low-risk areas help smooth the transition.
5. Maintaining autonomy as systems evolve
Implementing and maintaining autonomous testing requires periodic tuning as architectures, interfaces, and APIs change. Without proper upkeep, the autonomous testing system may drift or produce irrelevant scenarios. Continuous monitoring and cross-team collaboration keep the system aligned with evolving testing needs.
The Role of Human QAs in the Autonomous Testing Era
As autonomous QA becomes more capable, the role of human QAs does not disappear — it evolves. Instead of spending time on brittle scripts and repetitive actions, testers shift toward high-value work that autonomous systems cannot fully replace. Modern QA roles focus on guiding intelligence, validating decisions, and ensuring the system behaves responsibly within the broader testing lifecycle.
Strategic decision-making and risk analysis
Human testers define priorities, interpret risks, and shape the overall testing approach. While autonomous systems can execute and adapt, determining what matters most still depends on human understanding of business logic and user expectations.
Designing meaningful scenarios and evaluation criteria
Even with AI-driven capabilities, testing activities rely on QAs to design boundaries, specify intent, and provide context that autonomy can learn from. Humans determine edge cases, user journeys, and acceptance criteria that guide autonomous behavior.
Supervising AI-driven decisions and maintaining trust
Because autonomous testing influences what gets tested and how tests adapt, QAs review decisions, validate corrections, and ensure the system does not drift from the product’s intended behavior. Trust grows through oversight, not blind reliance.
Exploratory and usability-focused testing
Autonomy excels at executing patterns, but testing needs such as usability validation, emotional response, accessibility insight, and UX flow evaluation still rely on human intuition. Exploratory work continues to uncover issues that automation testing cannot identify.
Cross-team collaboration and quality leadership
Modern QA roles bridge development, DevOps, product, and data teams. As autonomy increases speed and reduces repetitive tasks, QAs gain more time for communication, management, analysis, and adopting quality culture across the organization.
Build or transform your testing process to maximize its value with us.
How to Choose an Autonomous Testing Tool That Works for You
Selecting the right autonomous testing tool requires more than comparing features. Teams must evaluate how well the solution fits their architecture, workflows, and long-term testing needs. Because autonomous testing influences decision-making across the entire testing lifecycle, choosing the right platform ensures stability, transparency, and reliable scaling.
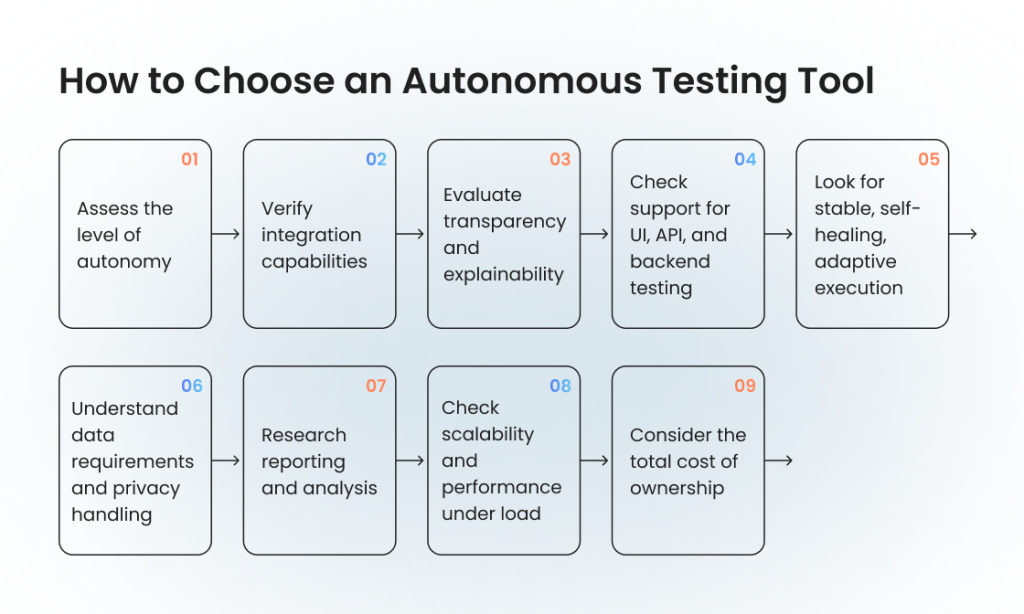
Here is how to choose a tool that meets your team’s needs and expectations:
- Assess the level of autonomy. Some tools provide only AI-assisted authoring, while others deliver full adaptive execution and scenario generation. Choose a solution that matches your current maturity but can grow with your testing approach.
- Verify integration capabilities. A strong tool should integrate smoothly with your CI/CD, version control, issue trackers, and environments. Difficult integrations reduce the value of autonomy and increase operational friction.
- Evaluate transparency and explainability. Because autonomous systems adapt tests automatically, teams must see why decisions were made. Clear logs, rationale summaries, and human-review workflows are essential for long-term trust.
- Check support for UI, API, and backend testing. Modern systems rarely rely on UI alone. The right solution should provide broad coverage across interfaces, services, data flows, and integrations to ensure comprehensive testing activities.
- Look for stable, self-healing, adaptive execution. Self-healing should handle changes in UI, APIs, and component structures reliably. A tool that frequently misinterprets changes will create noise instead of reducing maintenance.
- Understand data requirements and privacy handling. Review how the tool manages application data, logs, and analytics. Strong masking options, environment isolation, and compliance features help protect sensitive information without limiting autonomous capabilities.
- Research reporting and analysis. Tools should offer actionable insights, not just pass/fail results. Prioritization suggestions, anomaly detection, and clear root-cause explanations strengthen the overall testing process.
- Check scalability and performance under load. As test suites grow, the platform should maintain consistent execution speed and stability. Cloud readiness, parallelization, and elastic infrastructure support are critical for scaling autonomy.
- Consider the total cost of ownership. Long-term value depends on reduced maintenance, faster cycles, and fewer false failures. Choose a tool that enhances efficiency rather than one that simply adds more automation.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples of Autonomous Testing
Autonomous testing delivers the strongest value in environments where change is constant and complexity grows faster than scripted automation can manage. Here are several industry-focused examples illustrating how autonomy supports real product requirements and testing needs.
A rapidly scaling B2B SaaS platform ships new UI components daily using feature flags and iterative design experiments. Scripted tests fail constantly as elements shift, causing delays in every regression cycle. Autonomous testing stabilizes delivery by self-healing selectors, adapting flows during execution, and prioritizing checks based on the features customers interact with most.
A global fintech provider operates dozens of microservices that handle onboarding, payments, risk scoring, and fraud detection. API contracts evolve weekly, and silent integration failures can lead to compliance exposure. Autonomous testing detects drift, reevaluates transaction paths end-to-end, and surfaces emerging risks earlier than traditional automation testing, strengthening both speed and regulatory alignment.
A leading digital health platform integrates patient records, device data, and scheduling flows across multiple healthcare systems. Even small backend adjustments break complex clinical interactions, making manual validation slow and error-prone. Autonomous testing adapts to variable medical data, verifies high-risk patient journeys, and uncovers interoperability gaps, helping the platform maintain safety and reliability.
A large logistics and supply-chain platform relies on distributed microservices for routing, warehouse automation, inventory synchronization, and carrier integrations. Independent service updates frequently break downstream workflows without immediate visibility. Autonomous testing continuously monitors API behavior, validates asynchronous event flows, and identifies performance regressions caused by service interactions long before they reach production.
An AI-enabled content and automation platform depends on LLM-driven features that generate dynamic outputs for enterprise users. Scripted automation cannot reliably validate non-deterministic responses. Autonomous testing evaluates full user journeys, flags inconsistent or risky model outputs, and tracks behavioral drift over time, ensuring safe, predictable operation of its AI-powered capabilities.
The Future of Autonomous Testing: Where It Will Go in the Coming Years
The next era of autonomous testing won’t be defined by faster execution alone — it will be shaped by deeper intelligence, tighter integration with engineering ecosystems, and more reliable decision-making. As AI continues to mature, autonomous testing will extend beyond supporting automation and begin contributing directly to engineering strategy and product quality. Here are the key trends giving us the idea of where autonomous QA may end up in the near future.
1. Smarter reasoning and multi-agent collaboration
Autonomous testing is moving toward systems that can coordinate multiple AI-driven agents. These agents will explore different parts of the application, share findings, and form collective insights. This shift will allow autonomous testing to understand complex behaviors rather than just execute flows.
2. Deep integration with observability and real user signals
Future platforms will pull telemetry, logs, and production trends directly into the testing approach. Autonomous testing uses AI to correlate failures with performance changes, user behavior, or service degradation, creating a feedback loop that keeps the testing lifecycle aligned with real-world usage.
3. Scenario generation based on real risks, not assumptions
Instead of relying on predefined scripts, future models will interpret architecture diagrams, API schemas, user journeys, and design documents to propose new scenarios automatically. This will push automation from scripted coverage to behavior-driven exploration.
4. Continuous evolution of tests through model-driven learning
As autonomous testing involves AI, systems will learn from millions of past executions and refine tests dynamically. Models will identify brittle areas, optimize sequences, and restructure suites to reduce duplication and noise, creating test portfolios that evolve with the product.
5. Expanded support for AI and ML systems
As intelligent applications become mainstream, testing AI systems will join the core responsibilities of autonomous testing. Future tools will evaluate model drift, prompt variability, safety constraints, and reliability, bridging the gap between traditional automation testing and modern AI evaluation.
6. Greater emphasis on governance, safety, and explainability
As autonomy increases, organizations will demand clearer oversight. Future platforms will provide transparent explanations of decisions, configurable guardrails, and policy-driven controls to keep AI-driven behavior predictable and auditable.
7. Seamless collaboration between humans and autonomous systems
Human QAs will remain essential. The future lies in workflows where testers guide the system, validate reasoning, and make final risk decisions while autonomy handles operational work. This hybrid model will redefine efficiency and elevate QA roles across the engineering organization.
Final Thoughts
Above everything else, autonomous testing represents a shift in how engineering teams think about quality. Rather than relying on brittle scripts or manual effort, organizations can now use adaptive systems that learn from behavior, respond to unexpected changes, and keep the testing lifecycle aligned with the pace of modern software delivery. It is not a replacement for human insight, but a powerful extension of it — one that frees QAs to focus on strategy, risk, and deeper product understanding.
As architectures grow more dynamic and AI becomes integrated across the stack, the value of autonomy will only increase. Teams that adopt intelligent testing early gain not just faster pipelines, but more resilient systems and a clearer view of product health. Autonomous testing isn’t a future vision anymore — it’s a practical way to build software that stays stable as everything around it continues to change.
FAQ
 How long does it take to see value from autonomous testing?
How long does it take to see value from autonomous testing?
Most teams see benefits within a few weeks, especially in reduced test maintenance and faster regression cycles. Full value emerges as the system learns your product, usually over one to three months depending on complexity and release frequency.
 Is autonomous testing meant to replace my QA team?
Is autonomous testing meant to replace my QA team?
No. It reduces repetitive work but doesn’t replace human judgment. QAs still design scenarios, assess risks, supervise AI-driven decisions, and handle exploratory and usability testing. Autonomous testing strengthens teams by freeing them from maintenance-heavy tasks.
 Will autonomous testing work with legacy systems or older tech stacks?
Will autonomous testing work with legacy systems or older tech stacks?
Yes, in most cases. Tools that rely on behavioral understanding rather than selectors or UI frameworks often work well with legacy applications. The key constraint is access — if the system can interact with the app, it can usually learn it.
 What skills do testers need to work effectively with autonomous testing?
What skills do testers need to work effectively with autonomous testing?
Primarily analytical and strategic skills rather than scripting-heavy ones. Testers benefit from understanding risk modeling, basic AI behavior, system architecture, and how to evaluate autonomous decisions. Communication and cross-team collaboration become more important as well.
 Is autonomous testing expensive to maintain?
Is autonomous testing expensive to maintain?
Maintenance is lower than traditional automation, but not zero. The system still needs guardrails, reviews, environment stability, and occasional fine-tuning. The goal isn’t eliminating maintenance but shifting it from mechanical script fixing to higher-level supervision.
Jump to section
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!