Modern engineering teams ship software faster than ever, but speed alone doesn’t guarantee quality. Even with strong pre-release testing, some issues only reveal themselves under real-world pressure, when real users interact with features, infrastructure behaves unpredictably, and traffic patterns shift without warning. That’s where shift-right testing comes in, giving teams the visibility and resilience they need to deliver reliable software at scale.
In our previous article on shift-left testing, we explored how preventing defects early can transform the development process. Now, we are looking at the other side of the equation: how shifting right helps validate performance, user experience, and stability after deployment. Together, these approaches form a balanced, modern testing strategy that supports confident releases and continuous improvement. Let’s find out what shift-right testing stands for, how it’s different from the shift-left approach, and how to combine both in a powerful testing strategy.
Key Takeaways
- Shift-right testing extends quality checks into real-world environments to validate performance, resilience, and user experience after deployment.
- Shift-left testing prevents defects early by improving code quality, clarifying requirements, and strengthening the development process.
- Combining shift-left and shift-right creates a continuous feedback loop that improves software quality across the entire lifecycle.
- Shift-right testing provides valuable insights into real user behavior that cannot be fully simulated in pre-release environments.
- Agile and DevOps teams rely on shift-right to validate frequent releases and ensure stable performance in production.
- Safe rollout strategies, such as canary releases and feature flags, help teams test in production without exposing the full user base to risk.
- Real-time monitoring is essential for detecting issues quickly and understanding system behavior under real-world conditions.
- Chaos engineering and controlled failure tests help teams assess system resilience and prepare for unexpected events.
- Gradual adoption of shift-right practices reduces risk and helps organizations build confidence in testing after deployment.
- A unified approach to testing improves release confidence and ensures that both preventative and operational insights guide product decisions.
What Is Shift-Right Testing?
Shift-right testing is a testing approach that extends validation into staging and the production environment to capture how a system behaves under real-world conditions. Instead of stopping quality checks after pre-release stages, teams run specific testing activities much later in the development process, often while a new feature is gradually exposed to a small subset of users. This helps QA and engineering teams observe real user interactions, gather valuable insights, and confirm that the software development effort delivers the expected user experience.
Shifting right emerged as a natural evolution of DevOps and continuous delivery practices. Modern applications rely on distributed architectures, frequent releases, and rapid deployment cycles. As a result, teams need real-time visibility into system behavior, performance, and stability after features are deployed. Shift-right testing provides that visibility, enabling teams to detect defects that only appear under real-world traffic patterns, infrastructure variations, or unexpected usage scenarios.
Key principles of shift-right testing
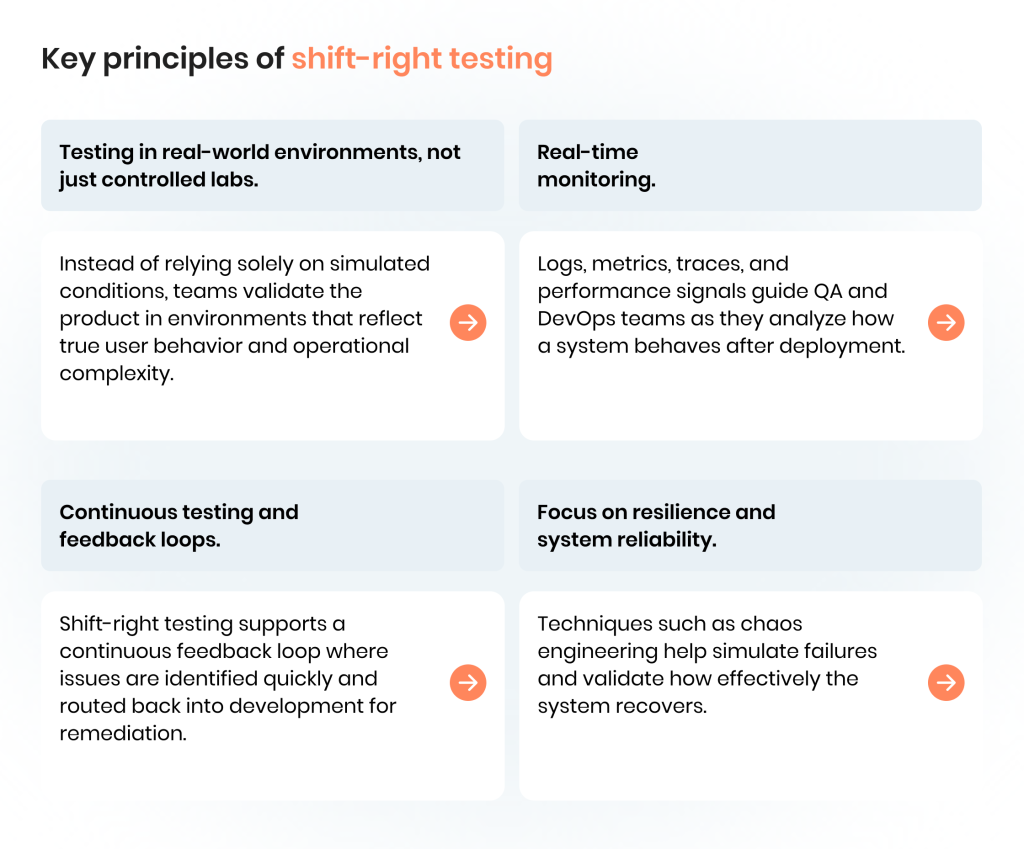
Shift-right testing is guided by a few essential principles that set it apart it from traditional testing performed earlier in the development lifecycle:
- Testing in real-world environments, not just controlled labs. Instead of relying solely on simulated conditions, teams validate the product in environments that reflect true user behavior and operational complexity.
- Real-time monitoring. Logs, metrics, traces, and performance signals guide QA and DevOps teams as they analyze how a system behaves after deployment.
- Continuous testing and feedback loops. Shift-right testing supports a continuous feedback loop where issues are identified quickly and routed back into development for remediation.
- Safe, gradual exposure of new features. Teams carefully deploy changes to a small subset of users to minimize risk while still capturing accurate feedback.
- Focus on resilience and system reliability. Techniques such as chaos engineering help simulate failures and validate how effectively the system recovers.
Together, these principles allow teams to gain insights that earlier testing stages may not reveal, especially those tied to scale, traffic spikes, or unpredictable real-world patterns.
Core shift-right testing activities
Shift-right testing includes a range of actions that evaluate how a system performs under actual operational load and real user conditions:
- Canary and staged releases. Deploying a new feature to a subset of users enables teams to observe its impact before rolling it out globally.
- A/B experiments and UX telemetry. Real user behavior provides evidence of how well features meet user expectations and where issues may occur.
- Production performance testing. Unlike pre-release load tests, this validates responsiveness, throughput, and stability under genuine traffic patterns.
- Chaos engineering and resilience checks. Teams intentionally simulate failures — network outages, node crashes, or latency spikes — to ensure the system remains stable.
- Synthetic monitoring and real-time alerts. Automated checks continuously measure performance and availability across environments.
- Monitoring and testing of critical user journeys. End-to-end testing in production helps ensure core flows remain functional after each deployment.
These activities combine to create a data-rich, grounded view of software quality — something that cannot be fully achieved through shift-left testing alone.
What Is Shift-Left Testing?
Shift-left testing focuses on detecting a bug or defect as early as possible by moving testing activities toward the beginning of the development process. Instead of waiting for the development phase to finish, teams start testing early — often during requirements, design, and initial coding. This approach is common in agile testing, where rapid iterations and short feedback loops depend on preventing issues before they reach later stages of the software development lifecycle.
Shift-left testing helps teams improve code quality, reduce costly rework, and create a smoother development cycle. While shift-right testing validates how a system behaves in the production environment, shift-left complements it by catching foundational issues that could otherwise slow down or destabilize real-world releases.
Key principles of shift-left testing

Before diving into specific practices, it’s important to understand the foundation of shift-left testing. At its core, this approach emphasizes prevention: identifying issues at the earliest possible stage, reducing risk, and ensuring that development decisions are validated long before deployment. These principles keep teams aligned and make the entire software development process more predictable:
- Early testing strengthens quality. By validating requirements and architecture before development accelerates, teams ensure that problems are caught early rather than after deployment.
- Fast feedback for developers. Automated testing and continuous integration give developers quick visibility into defects introduced during implementation.
- Preventative approach to software quality. Shift-left focuses on avoiding defects rather than reacting to them later, reducing the overall risk and cost.
- Collaboration across QA and engineering. The approach embeds QA into planning, design, and coding activities, creating a shared responsibility for quality.
Core shift-left testing activities
Shift-left testing relies on practical, structured activities that help teams enforce quality from the very beginning. These activities are typically lightweight, repeatable, and highly automated, making them suitable for agile environments and frequent release cycles:
- Unit and API-level validation to ensure core logic behaves correctly before integration.
- Static analysis and code reviews to maintain strong code quality throughout development.
- Functional testing early in the development cycle to confirm that critical flows behave as expected.
- Test automation integrated into CI pipelines to give teams immediate visibility into regressions.
- Early performance and security checks that prevent architectural issues from surfacing during later stages.
Our Webinar on Shift-Left Testing: How and Why Smart Teams Test Earlier
Shift-Left vs. Shift-Right: What’s the Real Difference?
Shift-left vs. shift-right is not a question of choosing one approach over the other. Both support different parts of the software development cycle and help with different categories of risk. Shift-left testing prevents issues early, while shift-right testing validates how the application behaves under real-world conditions after deployment. Together, they form a testing strategy that supports higher software quality, faster releases, and more reliable user experience.
While shift-left focuses on early testing, shift-right introduces testing in the production environment and relies on real-time data, monitoring, and controlled exposure of new features. Understanding where each approach fits helps teams apply the right testing techniques at the right stage of the development lifecycle.
How both approaches enhance software quality
Shift-left and shift-right testing each target specific weaknesses that traditional testing sometimes overlooks. Shift-left reduces defects early in the development process, improves code quality, and keeps the development cycle efficient. Shift-right testing, on the other hand, focuses on how the application behaves in real-world conditions, where infrastructure, traffic, and user behavior can reveal issues that did not appear in controlled pre-release testing.
By combining the two, teams create a continuous feedback loop that strengthens resilience, improves user experience, and ensures that quality assurance is not limited to a single phase.
When to apply each approach across the SDLC
Shift-left testing is most effective during the early planning, design, and coding stages, where fast feedback and prevention matter most. Shift-right testing becomes essential once the application reaches later stages — staging, release, and live operation — where real user interactions provide data that cannot be simulated accurately.
Together, they support a complete testing approach across the entire development lifecycle and help maintain software quality throughout continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines.
Let’s break down the differences, best use cases, and limitations of both approaches one more time.
| Aspect | Shift-Left Testing | Shift-Right Testing |
| Primary goal | Prevent defects early and ensure strong code quality | Validate behavior under real-world conditions and improve resilience |
| Focus | Requirements, design, architecture, unit logic | User experience, performance, reliability, real user interactions |
| Timing | Early in the development process | After deployment, often in staging or the production environment |
| Key activities | Static analysis, unit tests, API checks, functional testing | Canary releases, A/B tests, monitoring and testing, chaos engineering |
| Tools used | CI tools, automated testing frameworks, code analysis tools | Application performance monitoring platforms, feature flags |
| Strengths | Early detection, lower cost of fixing issues | Valuable insights from real-world usage, better release confidence |
| Limitations | Cannot predict production-specific scenarios | Requires safe rollout strategies to minimize risk |
| Best use cases | Stable codebase, iterative development, early-stage refinement | Validating new feature behavior, monitoring releases, improving reliability |
The Biggest Benefits of Shift-Right Testing
Shift-right testing gives teams visibility into how their application performs under real-world conditions — something shift-left alone cannot fully deliver. By validating features in the production environment and observing real user behavior, engineering teams gain insights that help improve user experience, resilience, and overall software quality. Below are the biggest advantages of shifting right:
- Real user insights that can’t be simulated. Shift-right testing captures real user interactions, traffic patterns, and behaviors that traditional testing environments often miss. This provides valuable insights into how features perform in real-world conditions and helps teams enhance software based on actual usage.
- Early visibility into production-specific defects. Some issues only appear after deployment, such as configuration mismatches, environment differences, or unpredictable spikes in traffic. Shift-right testing helps detect these defects quickly and route them back into the development cycle.
- Better performance validation under authentic load. Pre-release performance tests are helpful, but they can’t mirror the true complexity of live systems. Testing in the production environment allows teams to confirm responsiveness, throughput, and latency based on real-time metrics.
- Improved resilience and reliability. Techniques like chaos engineering and failure simulation help teams evaluate system resilience in a safe, controlled way. This ensures the system remains stable even when unexpected conditions occur.
- Safer releases through gradual rollout strategies. Canary releases, feature flags, and controlled exposure to a small subset of users allow teams to test how a new feature behaves without risking the entire user base. This approach reduces deployment-related risk and improves release confidence.
- A stronger continuous feedback loop. By observing production behavior and real user feedback, engineering teams get actionable data to inform fixes, optimizations, and future iterations. This accelerates decision-making and supports continuous testing across the lifecycle.
- Faster detection and remediation of production issues. Real-time monitoring and alerting highlight anomalies immediately after deployment, reducing Mean Time to Resolve and preventing broader service disruption. This is especially important for applications that rely on continuous integration and continuous delivery.
- Enhanced user experience driven by real metrics. Shift-right testing surfaces usability issues, performance friction, and behavioral patterns that direct testing often overlooks. These insights help teams align releases with user expectations and user preferences.
- Validation of new feature behavior before full rollout. Testing a new feature in production provides evidence of its stability, performance, and impact on user journeys. Teams can refine or revert quickly if needed, increasing release stability.
Find out how shift-right testing can transform your QA process
Shift-Right Testing in Agile and DevOps
Agile and DevOps practices rely on rapid iterations, continuous delivery, and short release cycles, making it essential to validate how software behaves after each deployment. Shift-right testing supports this reality by extending testing activities into production-like and live environments, where real-time data and user behavior offer insights that traditional testing simply cannot provide. Instead of treating quality as something verified only before release, DevOps teams use shift-right testing to maintain software quality throughout ongoing releases, operational changes, and infrastructure updates.
Modern delivery pipelines depend on automation, continuous monitoring, and fast reaction to change. Shifting right fits naturally into this culture: it helps teams detect issues quickly, maintain resilience, and continuously improve the user experience across every release.
How shift-right strengthens agile delivery
In agile environments, teams iterate quickly, introduce frequent changes, and continually refine the product based on user feedback. Shift-right testing adds an additional layer of validation by showing how each increment behaves under real-world conditions. This helps agile teams gain insights that inform future sprints, highlight performance risks, and reveal unexpected user interactions that aren’t visible during early testing.
Shift-right testing also supports agile principles by creating tighter feedback loops. As new features roll out to a small subset of users, teams collect real-time data and adjust their backlog items accordingly. The result is a development process where decisions are informed not only by planned requirements and early testing, but by true operational evidence.
Why shift-right is essential in DevOps pipelines
DevOps teams rely on continuous integration, continuous delivery, and rapid deployment cycles, all of which require confidence in how software behaves after release. Shift-right testing provides that confidence. By incorporating monitoring and testing into the production environment, teams can validate performance, resilience, and user experience as part of the ongoing release process.
Techniques such as canary releases, feature toggles, and automated rollback mechanisms allow DevOps teams to test in production safely. Monitoring tools provide metrics, traces, and alerts that feed into a continuous feedback loop, helping engineers detect defects, track real-time performance patterns, and respond to issues before they affect a wider user base. In this way, shift-right testing becomes a natural extension of DevOps culture — one that prioritizes experimentation, automation, and constant improvement.
Combining Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing: A Winning Testing Strategy
Using shift-left and shift-right together gives engineering teams a complete view of quality across the entire development lifecycle. Instead of relying solely on early testing or late-stage validation, a unified strategy creates a continuous feedback loop that improves software quality, strengthens resilience, and ensures every release aligns with real user expectations. Below are the key elements of how these two approaches work together effectively.
Early prevention meets real-world validation
Shift-left testing catches logical flaws, architectural issues, and defects early in the development process, while shift-right testing confirms whether those decisions hold up in real-world conditions after deployment. Together, they reduce risk and prevent issues from slipping into production unnoticed.
A continuous feedback loop across the lifecycle
Combining both approaches creates a feedback loop that starts during design and coding and continues into live operation. Developers receive insights not only from automated tests but also from real-time metrics, user behavior, and operational data gathered after release.
Better alignment with user expectations
Shift-left ensures that requirements are clear and code quality remains high, while shift-right reveals how users actually interact with new features. This helps teams refine functionality based on real user preferences rather than assumptions made during early planning.
Improved resilience through complementary testing activities
Shift-left activities such as static analysis and functional testing build a solid foundation, while shift-right techniques like chaos engineering and monitoring strengthen a system’s resilience under unpredictable real-world conditions.
Safer, more confident releases
Early testing lowers the chance of pushing unstable features forward, and late-stage validation — using canary releases or controlled rollouts — ensures safer deployment. This combination supports frequent releases without compromising system stability.
Shared ownership of software quality
When both approaches are used together, QA, DevOps, and development teams collaborate throughout the software development cycle instead of working in isolated phases. This shared responsibility results in more consistent, reliable, and user-centric delivery.
A holistic testing strategy that grows with the product
Shift-left lays the groundwork for maintainable, high-quality code, while shift-right provides ongoing insights as the system evolves. This dual model supports long-term scalability and continuous improvement across every release.
Let us build the perfect end-to-end QA strategy for your product.
Best Practices of Shifting Right
Shifting right is most effective when it follows a clear, disciplined framework. Because testing in later stages interacts closely with real-world systems and real user behavior, teams need structured practices that minimize risk while maximizing insight. Here are the most important best practices for implementing shift-right testing safely and effectively.
Use safe rollout strategies to reduce risk
Techniques such as canary releases, feature toggles, and staged deployments allow teams to expose a new feature to a small subset of users before it reaches the full audience. This controlled approach helps detect issues early without compromising the overall user experience.
Integrate strong system monitoring
Shift-right testing depends on real-time metrics, logs, and traces to provide actionable feedback after deployment. Continuous monitoring tools give QA and engineering teams visibility into performance, resource usage, and user interactions, enabling them to identify defects as soon as they appear.
Automate production checks where possible
Automation is essential for continuous testing in live or production-like environments. Synthetic monitoring, automated alerting, and scheduled validation help teams detect anomalies quickly, maintain resilience, and ensure that critical user journeys work consistently across releases.
Combine real user data with synthetic testing
Real user behavior offers insights that lab environments cannot fully capture, but synthetic checks help validate predictable paths and performance baselines. Using both together ensures balanced coverage and a more accurate understanding of system behavior.
Simulate failures to improve system resilience
Chaos engineering and controlled fault injection help teams validate how the system responds to disruptions such as latency spikes, instance failures, or dependency outages. This strengthens system resilience and reduces the chances of unexpected production incidents.
Feed insights back into earlier stages
Shift-right testing isn’t only about identifying issues after deployment — it’s also about improving the earlier phases of development. Teams should route insights from production monitoring, user behavior patterns, and real-time data back into their shift-left practices to enhance software design and test coverage.
Establish clear ownership and collaboration across teams
Shift-right requires coordination between QA, DevOps, and engineering to be effective. When teams work together on monitoring, performance analysis, and release strategies, they ensure that testing activities align with operational goals and long-term product quality.
Prioritize critical user journeys
Not every part of the application needs the same level of production testing. Focusing shift-right activities on high-traffic, revenue-critical, or risk-prone flows helps teams allocate effort effectively while protecting the most important aspects of the user experience.
How to Adopt Shift-Right Testing Without Increasing Risk

Adopting shift-right testing doesn’t mean having to expose your users or infrastructure to unnecessary danger. When implemented thoughtfully, shifting right enhances reliability instead of compromising it. The key is to build the right safeguards, prepare teams for new workflows, and ensure your shift-right efforts are tightly aligned with operational priorities and user expectations. Here is how you can minimize risk on your project while maximizing the benefits.
1. Start with a clear definition of what you will and won’t test in production
Shift-right doesn’t apply to every scenario. Teams should identify which features, flows, and metrics actually benefit from testing in the production environment and which should stay in staging. This prevents over-testing, reduces noise, and ensures testing aims are tied to real user outcomes.
2. Establish strict guardrails before exposing anything to real users
Before any feature reaches even a small subset of users, teams need rules for rollback conditions, error budgets, alert thresholds, and acceptable performance baselines. These boundaries make testing in production predictable, safe, and fully reversible.
3. Align shift-right adoption with business-critical priorities
Shift-right testing should support business KPIs, not contradict them. Teams must determine which user interactions, customer segments, or workflows are sensitive and require extra caution, and which ones can safely be used to gain insights through controlled exposure.
4. Make monitoring a prerequisite, not an afterthought
Teams should treat monitoring capabilities as part of the development lifecycle, not a last-minute addition. Without complete visibility — metrics, traces, logs, and real-time signals — shift-right efforts can create blind spots that obscure defects rather than highlight them.
5. Validate your data pipelines before testing in production
Shift-right testing relies heavily on accurate telemetry. If data pipelines, metrics, or analytics tools are unreliable, the insights gained from real-world conditions will be misleading. Ensuring data integrity up front prevents poor decision-making later.
6. Introduce shift-right in stages instead of going all-in
Teams new to shift-right should begin with limited-scope tests — validating a single flow, releasing a minor improvement behind a flag, or observing a UI update with internal staff only. Gradual expansion helps refine processes and reduce risk.
7. Use operational rehearsals to prepare teams for live incidents
Before running any real-world experiments, teams benefit from practicing how they’ll respond to unexpected behavior. Tabletop exercises, dry-run drills, and simulated outages help engineers build confidence and ensure your shift-right program is ready for real-time challenges.
8. Review and refine your testing model after each release
Shift-right adoption isn’t static. After every controlled launch, teams should evaluate what worked, what triggered alerts, and what types of user behavior revealed unexpected findings. This reflective loop ensures the testing approach evolves and becomes safer over time.
The Complete Guide to the Software Testing Process: Stages, Deliverables, Best Practices, and More
Final Thoughts
Shift-right testing isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a mindset shift that gives teams the confidence to evolve their products in real time. By embracing real-world signals, controlled experiments, and continuous learning, engineering teams turn production from a risk into a strategic advantage.
When combined with the preventative strength of shift-left, shifting right completes a full-circle approach to quality. Together, these practices help teams deliver software that’s not only stable and resilient, but also deeply aligned with how users interact, behave, and expect it to perform.
FAQ
 Is shift-right testing the same as testing in production?
Is shift-right testing the same as testing in production?
Not exactly. Testing in production is one part of shift-right, but the approach also includes monitoring, user behavior analysis, controlled rollouts, and resilience testing. It’s a broader strategy that validates how the system performs under real-world conditions, not just a single activity.
 What types of issues show up only when shifting right?
What types of issues show up only when shifting right?
Shift-right often reveals performance bottlenecks, configuration problems, integration issues, and unexpected user behavior. These are hard to reproduce in test environments because they depend on real traffic, real data, and real-world infrastructure conditions.
 Can small teams or startups adopt shift-right testing effectively?
Can small teams or startups adopt shift-right testing effectively?
Absolutely. Many smaller teams start with basic system monitoring and canary releases. Shift-right doesn’t require enterprise-level resources; it simply requires thoughtful scoping, controlled exposure, and clear goals for what you want to learn after deployment.
 Does shift-right replace traditional pre-release testing?
Does shift-right replace traditional pre-release testing?
No. Shift-right complements shift-left and traditional testing but does not replace them. You still need strong unit, integration, and functional testing to prevent defects early. Shift-right adds operational context and verifies that everything still behaves correctly under actual usage.
 What skills does a team need to adopt shift-right testing?
What skills does a team need to adopt shift-right testing?
Teams benefit from strong real-time monitoring knowledge, understanding of deployment strategies, familiarity with monitoring tools, and the ability to interpret real-time metrics. Collaboration across QA, DevOps, and engineering also becomes more important, since decisions affect live systems.
Jump to section
- Key Takeaways
- What Is Shift-Right Testing?
- What Is Shift-Left Testing?
- Shift-Left vs. Shift-Right: What’s the Real Difference?
- The Biggest Benefits
- Shift-Right Testing in Agile and DevOps
- A Winning Testing Strategy
- Early prevention meets real-world validation
- A continuous feedback loop across the lifecycle
- Better alignment with user expectations
- Improved resilience through complementary testing activities
- Safer, more confident releases
- Shared ownership of software quality
- A holistic testing strategy that grows with the product
- Best Practices of Shifting Right
- Use safe rollout strategies to reduce risk
- Integrate strong system monitoring
- Automate production checks where possible
- Combine real user data with synthetic testing
- Simulate failures to improve system resilience
- Feed insights back into earlier stages
- Establish clear ownership and collaboration across teams
- Prioritize critical user journeys
- How to Adopt Shift-Right Testing Without Increasing Risk
- 1. Start with a clear definition of what you will and won’t test in production
- 2. Establish strict guardrails before exposing anything to real users
- 3. Align shift-right adoption with business-critical priorities
- 4. Make monitoring a prerequisite, not an afterthought
- 5. Validate your data pipelines before testing in production
- 6. Introduce shift-right in stages instead of going all-in
- 7. Use operational rehearsals to prepare teams for live incidents
- 8. Review and refine your testing model after each release
- Final Thoughts
- FAQ
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!