Modern software delivery requires more than just coding — it demands a structured process that brings together business needs, development, and quality assurance into a single workflow. Application lifecycle management in testing gives organizations a clear overview of the software, ensuring that every step, from requirements to release, complies with defined software and testing needs. By treating QA as an integral part of the lifecycle rather than an afterthought, ALM helps teams establish clear stages of testing, define exit criteria for testing, and measure the effectiveness of testing across the project.
But how exactly can testing and development teams incorporate ALM testing practices to see real benefits and further improve software quality, scalability, and future-readiness? Today, we’ll explain what application lifecycle management is, what ALM involves, and how to integrate it in your software projects the smart way.
What is ALM in Testing?
Application Lifecycle Management in testing is the practice of managing software testing as an integral part of the application lifecycle. Rather than treating testing as a separate stage at the end of development, ALM in testing ensures that validation, verification, and quality checks are embedded throughout its lifecycle. This approach allows teams to maintain traceability between requirements, test cases, and delivered software, helping development teams align closely with business goals and compliance standards.
By incorporating ALM QA practices, organizations can better streamline workflows and connect development and testing activities in a coherent framework. ALM in software testing emphasizes continuous monitoring and validation, enabling testers to detect defects earlier, reduce rework, and ensure higher-quality software. It also supports both manual testing and ALM test automation, giving teams flexibility to adapt to project needs.
Ultimately, ALM testing provides teams with visibility across the entire lifecycle of a software application, helping prioritize efforts, validate results, and improve collaboration between different teams. By embedding testing at every stage, ALM strengthens the organization’s ability to deliver reliable, high-quality software while mitigating risks and enhancing stakeholder confidence.
Why Is ALM Important for Testing and QA?
Implementing ALM in testing provides organizations with a structured approach to quality assurance and helps integrate testing into the software development process from the very beginning. By embedding testing into every stage of the application lifecycle, ALM improves visibility, reduces risks, and ensures that software meets business, technical, and compliance requirements. Here is how ALM impacts software testing:
Strengthens ALM quality assurance, ensuring delivery of high-quality software aligned with business goals.
Integrates quality assurance into the software development process, ensuring testing is continuous rather than an afterthought.
Maintains traceability between requirements, test cases, and delivered software, helping teams validate functionality and compliance.
Enables ALM test management and ALM test automation, allowing QA teams to detect and resolve bugs earlier.
Supports continuous integration, providing real-time feedback and improving collaboration between development teams and testers.
Helps streamline workflows, prioritize high-risk areas, and reduce project risks across different teams.
Provides managers with visibility into quality metrics, progress, and risk areas, enabling better decision-making.
Release flawless software faster and at a lower cost with the right QA partner
Key Stages of Application Lifecycle Management
Understanding the stages of ALM is essential for effectively integrating testing and quality assurance into the software development process. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring that software is delivered reliably, efficiently, and in alignment with business and compliance requirements. Embedding ALM QA practices throughout the lifecycle allows organizations to maintain traceability, improve collaboration among different teams, and support continuous improvement of high-quality software. Here are the stages ALM processes typically include.
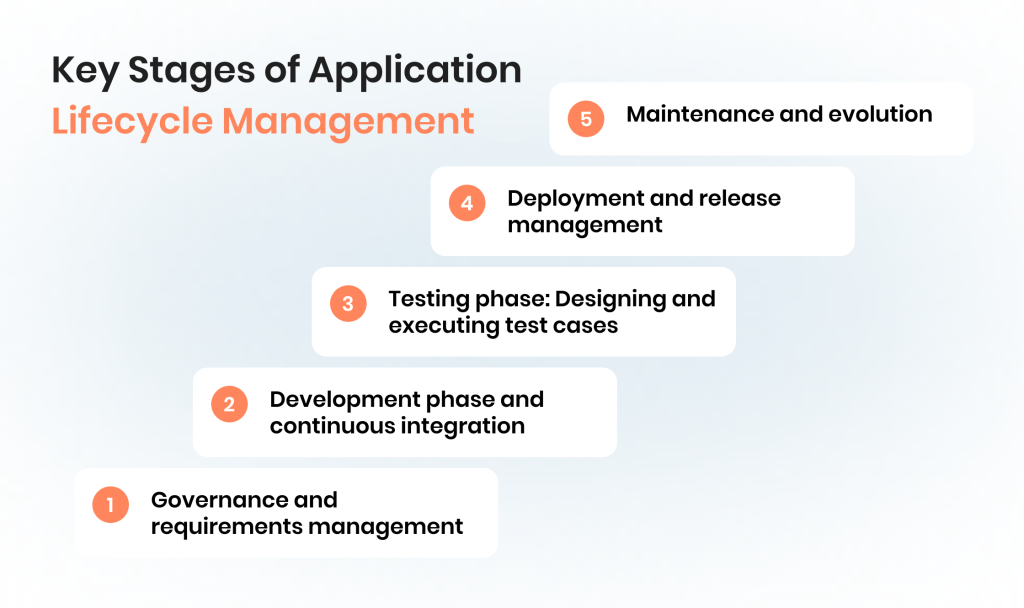
1. Governance and requirements management
At this stage, organizations define business, technical, and compliance requirements while establishing governance practices. Strong requirement management ensures that test cases are linked to business objectives and compliance standards, allowing QA teams to validate functionality early. Clear governance also supports risk management and provides visibility into priorities across the entire lifecycle.
2. Development phase and continuous integration
During the development phase, developers implement features while QA teams plan and integrate ALM test automation. Continuous integration allows code changes to be automatically tested, providing early detection of defects and improving collaboration between development teams and testers. This stage helps synchronize development and testing activities and maintain high-quality software throughout the software development process.
3. Testing phase: Designing and executing test cases
The testing phase focuses on creating, executing, and tracking test cases to ensure functionality, performance, and compliance. Teams may use manual testing alongside automated testing tools to cover critical workflows. Embedding ALM QA testing practices here ensures thorough testing and helps identify bugs before deployment.
4. Deployment and release management
Deployment involves releasing the software to production while minimizing risks and ensuring proper monitoring. ALM supports structured deployment and release management, maintaining traceability from requirements to the live system. This stage allows teams to detect issues early, verify software quality, and ensure that high-quality software reaches end users reliably.
5. Maintenance and evolution
After deployment, software is maintained and updated based on user feedback, performance monitoring, and changing business needs. ALM enables teams to automate regression testing, manage updates efficiently, and track ongoing compliance. Effective maintenance ensures software remains reliable and aligned with the organization’s application lifecycle management strategy.
The Role of QA in ALM
Quality assurance plays a central role in ALM in testing, ensuring that software meets business, technical, and compliance requirements at every stage. By integrating QA practices into the software development process and throughout the application lifecycle, organizations can maintain traceability, detect bugs early, and deliver high-quality software more efficiently. Here are the key responsibilities of QA within ALM.
Ensuring traceability and validation
QA maintains traceability between requirements, test cases, and delivered features, helping both development teams and managers validate progress and quality throughout the entire application development lifecycle. This ensures that software is in tune with business objectives, compliance requirements, and stakeholder expectations.
Integrating manual and automated testing
QA teams combine manual testing with ALM test automation to cover critical workflows efficiently. Automation allows teams to detect bugs early, reduce rework, and provide faster feedback during continuous integration, supporting smoother software delivery.
Streamlining collaboration
QA helps streamline communication and coordination between different teams, ensuring governance, compliance, and quality standards are consistently met. This fosters better alignment between QA, developers, and business stakeholders.
Supporting the full lifecycle
QA is involved from governance through maintenance, making testing a continuous activity rather than a final step. By embedding ALM QA practices throughout, organizations can deliver high-quality software and reinforce their application lifecycle management strategy.
ALM Solutions, Tools, and Methodologies for QA Teams
Quality assurance plays a central role in the application lifecycle, and the right ALM solutions help teams align governance, development phase, testing phase, and deployment.
When combined with specialized testing tools and modern methodologies, these technologies and solutions help QA teams streamline processes, design stronger test cases, and validate functionality throughout each stage. These components also ensure better collaboration between business stakeholders and engineers, reducing risks and enabling faster delivery.
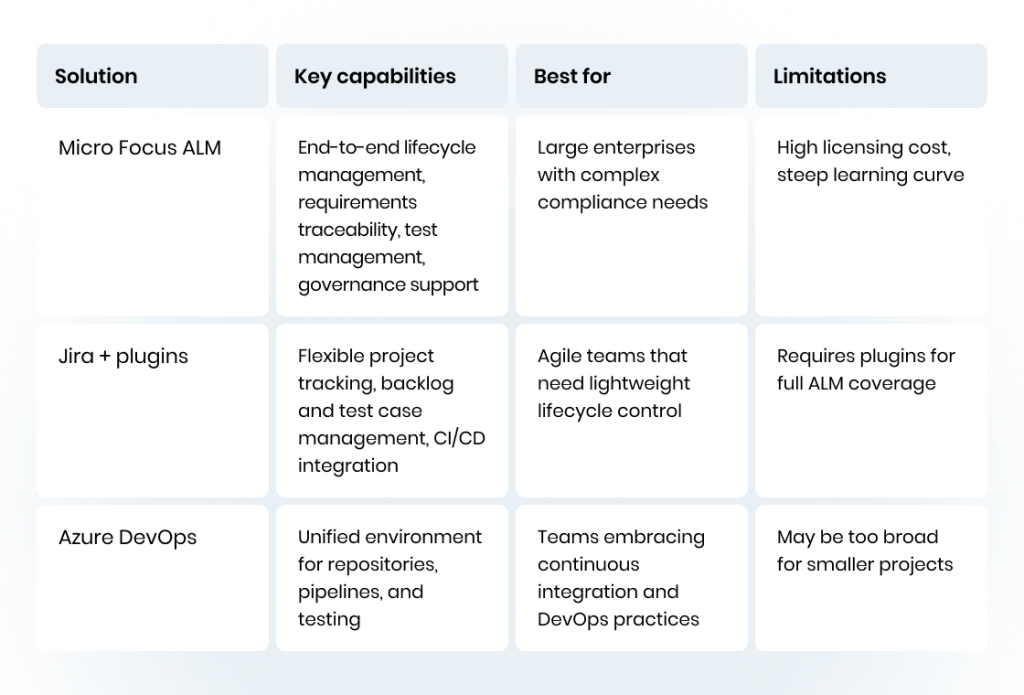
ALM solutions
Comprehensive ALM technologies serve as the backbone of lifecycle management. They cover everything from requirements gathering to release, enabling QA teams to maintain traceability, automate routine tasks, and ensure governance standards are met, in addition to offering a wide range of features used in traditional software development and testing. These are the solutions teams frequently use to manage the ALM product lifecycle and project management.
Testing tools
To maximize the value of ALM, QA teams rely on both specific ALM tools and general-purpose testing tools for a variety of tasks. ALM tools provide an opportunity to automate execution, manage test cases, and confirm that applications meet requirements. They integrate seamlessly with ALM platforms to improve coverage and efficiency. Here are the tools commonly used for testing within product lifecycle management.
| Tool | Capabilities | Best for | Limitations |
| Selenium | Automation of functional and regression testing across browsers | Web applications needing cross-platform coverage | Requires coding skills and ongoing maintenance |
| TestRail | Centralized test case management, detailed reporting, validation support | Structuring manual and automated test cases | Limited automation features |
| Jira + Xray | Test design, execution tracking, defect management inside ALM | Teams already working in Jira environments | Performance issues with very large test suites |
Methodologies shaping ALM
Application lifecycle management strategy is also shaped by the methodology a team adopts. Each methodology defines how requirements, testing, and deployment are handled, which in turn affects QA’s role. For the most part, these approaches match the development methodologies widely used by software development teams, but they also have a specific purpose within the application management context.
| Methodology | Key principles | Best for |
| Agile | Iterative development, frequent validation, adaptive governance | Teams seeking flexibility and rapid feedback loops |
| DevOps | Continuous integration, automated deployment, collaboration across development and testing | Organizations prioritizing speed and automation |
| Waterfall | Sequential stages, detailed documentation, structured governance | Highly regulated projects where predictability matters |
Building an Application Lifecycle Management Strategy for Testing
A well-defined application lifecycle management strategy ensures that testing is not an afterthought but an integrated part of the software development lifecycle. For QA teams, this means having a consistent framework for planning, executing, and improving testing practices while aligning with business goals and compliance requirements. A strong strategy enables teams to optimize ALM test management, increase collaboration, and deliver quality software more reliably.
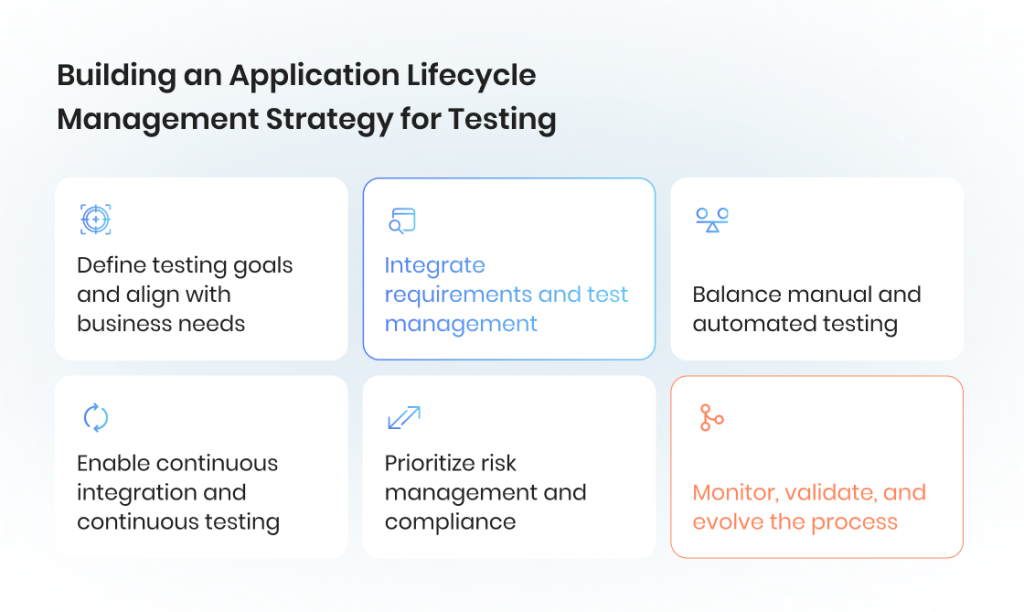
Here are the core steps to consider when building an ALM strategy focused on testing.
1. Define testing goals and align with business needs
Start by identifying what testing should achieve: defect reduction, compliance validation, performance monitoring, or end-to-end coverage. Linking QA objectives to the business case ensures that testing priorities support overall product success.
2. Integrate requirements and test management
Testing should be connected to requirement management to provide full traceability. This way, each test case maps back to a specific requirement, ensuring thorough coverage and simplifying compliance audits. Modern ALM solutions and testing tools help integrate requirements, test design, and defect tracking in one workflow.
3. Balance manual and automated testing
Both manual testing and ALM test automation are essential. Automated checks speed up regression cycles and validate frequent builds, while manual approaches cover exploratory and usability testing. Building the right mix increases testing efficiency and ensures critical areas aren’t overlooked.
4. Enable continuous integration and continuous testing
Embedding testing into the development phase and continuous integration pipelines helps detect bugs earlier. Automated regression, integration testing, and quality gates streamline releases and reduce risks in later stages.
5. Prioritize risk management and compliance
An effective ALM strategy accounts for risk management and regulatory compliance. QA teams must validate not only technical requirements but also industry standards, protecting the business from costly failures.
6. Monitor, validate, and evolve the process
An ALM strategy is not static. Teams should continuously monitor outcomes, track metrics, and validate whether testing contributes to delivering high-quality software. As the development process evolves, the ALM approach should adapt with new methodologies, tools, and stakeholder needs.
Not sure where your QA process stands or how to improve it?
Our QA consultants are here to help.
Challenges of ALM QA Testing
Even with all its advantages, applying ALM in testing comes with obstacles that QA teams and managers should be ready to address. Recognizing these challenges in advance helps organizations prepare realistic expectations and develop strategies to overcome them. These are the most common challenges team members can face when implementing ALM software testing practices.
Tool integration and compatibility
Many ALM technologies and testing tools are not designed to work seamlessly together. QA teams often struggle with connecting requirement management, test cases, automation frameworks, and defect tracking into one workflow. Poor integration can create silos and slow down the testing process.
Balancing automation and manual testing
While automation can streamline regression and repetitive checks, not all scenarios are suitable for automated execution. Teams must balance the effort spent on scripting with the need for exploratory, usability, and risk-based testing. Overreliance on either approach reduces the effectiveness of testing.
Governance and compliance requirements
Maintaining proper governance and meeting regulatory obligations can be complex in industries like healthcare, finance, or government. Without comprehensive traceability and documentation, QA may fall short during audits or fail to validate compliance-related requirements.
Resource allocation and skill gaps
Building an ALM-focused testing process requires not only tools but also skilled professionals. Teams often face constraints in budget, training, or time, making it difficult to implement ALM practices effectively across all stages of the lifecycle.
Adapting to evolving methodologies
Agile, DevOps, and hybrid models demand constant adaptation of testing processes. Without flexibility, QA teams risk being left behind by rapid release cycles, undermining the value of ALM.
Best Practices of ALM Quality Assurance
To make the most of ALM in testing, QA teams should follow proven practices that keep the process efficient, collaborative, and adaptable:
- Integrate QA early. Involve testers from the requirements and design stages to ensure traceability and reduce late-stage defects.
- Automate where it adds value. Apply automation for regression and repetitive tasks, while keeping room for exploratory and usability testing.
- Maintain clear governance. Establish rules for documentation, approvals, and compliance tracking to avoid gaps during audits.
- Streamline workflows. Connect tools for requirements, test management, automation, and defect tracking into one cohesive system.
- Validate continuously. Perform testing at each stage of the lifecycle, not just before release, to maintain consistent quality.
- Support collaboration. Encourage shared visibility and communication between developers, testers, and business stakeholders.
- Review and evolve strategies. Regularly revisit the application lifecycle management strategy to align with new technologies, methodologies, and business needs.
Final Thoughts
Application lifecycle management is not only about delivering software faster — it’s about delivering it better. By embedding QA at every point of the lifecycle, teams ensure that the process of testing is aligned with business objectives and compliance requirements. Testers gain the ability to design and manage meaningful test cases, apply different software testing approaches, and use the process of executing a program to catch risks early.
For organizations that want scalable and sustainable quality practices, ALM makes it possible to combine the principles of software testing with practical tools and methodologies. The result is more reliable software systems, better collaboration, and higher customer confidence, proving that when testing is treated as a strategic part of the lifecycle, the long-term benefits go far beyond defect detection.
Jump to section
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!