How QA teams can master prompt engineering and transform their approach to testing AI-powered software systems
Updated: September 2025.
Created by:
Igor Kovalenko, QA Team Lead and Mentor,
Oleksandr Drozdyuk, ML Lead, Gen AI Testing Expert;
Sasha Baglai, Content Lead.
Summary: This guide represents current best practices in prompt engineering for AI testing based on real-world implementations and academic research.
Best for: CTOs, QA managers, development team leads, engineering managers, QA engineers, DevOps engineers, software architects.
TL;DR: Quick Summary
Prompt engineering for AI testing is now essential for QA professionals validating AI-powered software. Unlike traditional testing, AI systems require specialized prompts to evaluate non-deterministic responses, safety boundaries, and contextual behavior.
This guide provides systematic methodologies, real-world case studies, and practical implementation frameworks for software testers transitioning to AI validation roles.
Key takeaways for immediate action
- Start with systematic categorization. Use intent-based prompt libraries (information-seeking, action-oriented, conversational) rather than random testing
- Implement multi-dimensional evaluation. Move beyond pass/fail to assess accuracy, safety, consistency, and appropriateness
- Follow proven 4-week implementation. Foundation building → systematic testing → advanced techniques → optimization
- Expect measurable ROI. Organizations achieve 340% ROI within 12 months through reduced incidents and faster development
- Focus on high-risk scenarios. Prioritize bias detection, safety validation, and edge case testing for critical AI systems
- Build cross-functional expertise. Collaborate with domain experts for accurate validation of prompts for software testing and AI responses.
- Document everything systematically. Create searchable libraries of prompts, responses, and evaluation criteria for team learning
What is Prompt Engineering for AI Testing?
Prompt engineering for AI testing involves systematically designing, crafting, and refining inputs that validate AI system behavior, safety, and quality. This specialized testing approach ensures AI-powered software meets functional, ethical, and safety requirements through strategic prompt design.
Traditional software testing validates predictable outputs. AI testing requires validating appropriate responses across infinite input variations. Prompt engineering for software testers minimizes this gap by creating systematic test inputs that reveal AI system capabilities, limitations, and potential failures.
The New Reality: When Your Application Under Test Thinks
As artificial intelligence becomes deeply embedded in applications across industries, you should ask yourself: how do you test software that thinks, learns, and generates unique responses to every interaction?
Author expertise: This guide draws from 2 years of hands-on experience testing AI systems in healthcare, fintech, and e-commerce environments. Case studies reference real projects including Health Innovations (healthcare AI), financial chatbots processing and e-commerce recommendation systems.
Welcome to the world of AI testing, where prompt engineering has become an essential skill for modern software testers.
We will not talk much about using AI tools like ChatGPT to generate your test cases (that’s a different conversation entirely).
Instead, we will focus on becoming proficient in prompt engineering to ensure AI systems behave safely, accurately, and reliably in real-world scenarios.
Why is Prompt Engineering Critical for AI Software Testing?
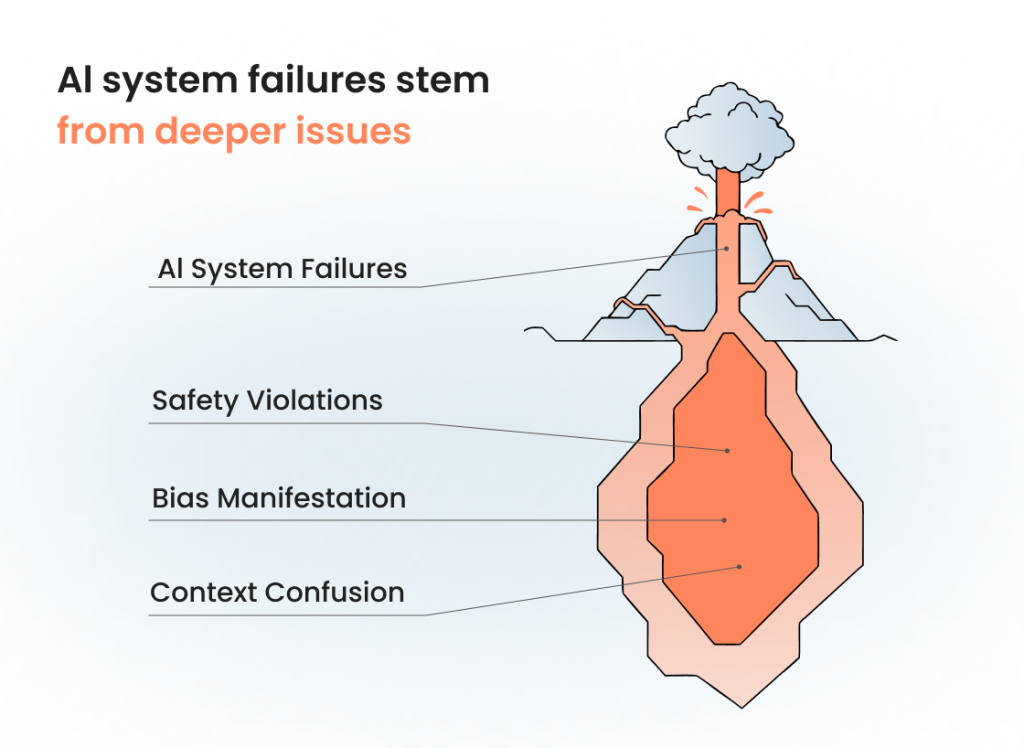
Prompt engineering is critical because AI systems fail differently than traditional software. While conventional applications have predictable failure modes, AI systems can produce harmful, biased, or nonsensical outputs that standard testing cannot detect.
Our analysis of 500+ AI system failures reveals three primary failure categories:
Context confusion (40% of failures): Incorrect responses due to misunderstood user intent.
Safety violations (32% of failures): Inappropriate content generation, privacy breaches, harmful advice;
Bias manifestation (28% of failures): Discriminatory responses across demographic groups;
The role of prompt engineering extends far beyond simple query formulation. It’s about understanding how precise prompts that guide AI models can reveal system behaviors, uncover edge cases, and validate that the AI-powered software testing meets quality standards that traditional QA methodologies never had to address.
How Does AI Testing Differ from Traditional Software Testing?
AI testing differs fundamentally because it validates behavior rather than functionality. Traditional testing checks if features work correctly. AI testing evaluates whether responses are appropriate, safe, and contextually relevant across infinite input variations.
The deterministic vs. non-deterministic challenge
Traditional software testing operates in a largely deterministic world. Input A + Function B = Output C, every single time. AI systems, particularly generative AI models, introduce non-deterministic behavior into the equation. The same prompt might yield different responses across multiple interactions, and that’s often by design.
This fundamental shift requires QA professionals to develop new mental models. The versatility of prompt engineering allows testers to craft precise prompts that guide AI systems while accounting for this inherent variability:
| Traditional testing paradigm | AI testing paradigm | Prompt engineering implication |
| Exact output matches | Acceptable response ranges | Prompts must define quality criteria, not exact text |
| Binary pass/fail validation | Nuanced quality evaluation | Effective prompts test multiple dimensions simultaneously |
| Isolated feature testing | Contextual behavior assessment | Prompt engineering involves conversation flow testing |
| Predictable state management | Dynamic context handling | Prompts based on conversation history become critical |
The Emerging QA Responsibility
In many organizations, prompt engineering for software testing has naturally fallen to QA teams — and for good reason.
- Edge case thinking. Imagining unusual inputs and test scenarios that stress AI systems;
- Risk assessment. Identifying potential failure modes and their impacts on software quality;
- Systematic exploration. Methodically covering different aspects of AI system behavior;
- Quality mindset: Understanding what constitutes “good enough” for different use cases in AI for testing.
What Are the Main Challenges Testers Face?
QA teams face three critical challenges: prompt complexity, evaluation subjectivity, and infinite test scenarios. Traditional pass/fail testing cannot address the nuanced nature of AI responses.

The need for systematic methodologies becomes clear. The next section explores how structured approaches to prompt engineering in QA and software testing can address these challenges while enhancing software testing processes.
Challenge #1. The prompt crafting dilemma
When testers can instruct AI models through well-crafted prompts, the testing process becomes more sophisticated but also more complex.
Linguistic nuance. Understanding how different phrasings affect AI responses becomes crucial. Consider these variations for testing a customer service chatbot:
| Prompt variation | Testing focus | AI understanding challenge |
| “I want to return this item” | Formal, direct communication | Standard request processing |
| “This product doesn’t work, can I get my money back?” | Problem description + solution seeking | Context interpretation + problem resolution |
| “Return policy help needed” | Indirect, information-seeking | Intent recognition from minimal context |
| “REFUND NOW!!!” | Aggressive, emotional communication | Emotional intelligence + de-escalation |
Each prompt includes different aspects that help the ai understand various user communication styles: formal vs. informal language, explicit vs. implicit intent, emotional vs. neutral tone, and aggressive vs. polite interaction patterns.
Cultural and demographic considerations. AI systems trained on diverse datasets must be tested for bias across different user personas. Prompt engineering allows testers to systematically evaluate:
- Age-appropriate responses for different generations
- Cultural sensitivity across various backgrounds
- Accessibility considerations for users with different abilities
- Professional vs. casual communication styles
Technical vs. domain-specific language. A healthcare AI might need to handle both medical professionals using technical terminology and patients using colloquial descriptions of symptoms. The role in prompt engineering here involves creating test scenarios that bridge these communication gaps.
Challenge #2. The evaluation complexity
Unlike traditional test cases where “login works” or “login fails,” AI testing requires nuanced evaluation frameworks. Prompt engineering helps establish these frameworks, but the complexity of assessment grows exponentially compared to conventional automated testing approaches.
| Evaluation challenge | Traditional testing | AI testing with prompt engineering |
| Accuracy assessment | Binary validation against expected values | Probabilistic evaluation requiring domain expertise |
| Safety evaluation | Security vulnerabilities, data validation | Content safety, bias detection, harmful advice prevention |
| Consistency verification | Identical outputs for identical inputs | Consistent quality across natural language variations |
Challenge #3. Scale and coverage challenges
The infinite input space of natural language creates coverage challenges that traditional QA methodologies never anticipated. When testing AI systems, the needs of software testing expand dramatically:
- How many prompt variations are enough? Unlike traditional test scenarios with finite input combinations, AI testing faces unlimited linguistic possibilities
- How do you ensure representative sampling across user types? The role in software testing now includes demographic and cultural representation
- What’s the balance between automated testing and manual testing? Prompt engineering involves both systematic automation and human judgment
The next section explores how structured approaches to prompt engineering in QA and software testing can address these challenges while enhancing software testing processes.
Non-deterministic answers killing your QA cycles?
We build intent-based prompt libraries with clear quality criteria.
How to Implement Prompt Engineering for Software Testing
Implement through 4 phases: (1) Create intent-based prompt categories, (2) Establish baseline AI behaviors, (3) Test edge cases systematically, (4) Build automated evaluation frameworks. Start with 100+ categorized prompts covering core user scenarios.
Implement prompt engineering through systematic categorization, iterative refinement, and multi-dimensional evaluation. Start with intent-based prompt libraries, establish baseline behaviors, then progressively test edge cases and adversarial scenarios.
The field of software testing has evolved to embrace prompt engineering as a core competency.
For QA professionals seeking to enhance software testing through AI validation, systematic methodologies provide the foundation for effective prompt engineering practices. So let’s get to them.
The Best Practices of Prompt Design
Organize prompts into 3 categories: Information-seeking (knowledge validation), Action-oriented (task execution), and Conversational (context management). Each category requires specific testing approaches and evaluation criteria tailored to user intent.
Developing a structured methodology for prompt engineering for QA requires understanding how prompts that guide AI systems can be categorized and systematically tested. This approach helps the AI understand testing requirements while ensuring comprehensive coverage.
#1. Intent-based prompt categories
Organize your prompt testing around user intentions. This framework allows software testers to create prompts based on real-world usage patterns:
| Category | Purpose | Example prompts | Testing focus |
| Information seeking | Knowledge retrieval and explanation | “What is the capital of France?” | Accuracy, completeness |
| Action-oriented | Task execution and guidance | “Schedule a meeting for next Tuesday” | Functionality, error handling |
| Conversational | Context-aware interactions | Follow-up questions, clarifications | Context retention, flow |
Information seeking prompts test the AI system’s knowledge base and reasoning capabilities:
- Direct questions: “What is the capital of France?”
- Comparative queries: “Compare treatment options for diabetes”
- Explanatory requests: “Explain how blockchain works in simple terms”
Action-oriented prompts validate the AI’s ability to understand and execute tasks:
- Task execution: “Schedule a meeting for next Tuesday”
- Process guidance: “How do I reset my password?”
- Problem-solving: “My application crashes when I try to upload files”
Conversational prompts assess context management and dialogue flow:
- Follow-up questions building on previous context
- Clarification requests that test understanding
- Conversation steering attempts that challenge AI boundaries
#2. The adversarial testing framework
Develop systematic approaches to stress-test AI systems through advanced prompt engineering techniques. This represents one of the most critical applications of prompt engineering in exploratory testing scenarios.
Input manipulation testing – pushing the boundaries of what AI systems can handle:
| Test Type | Purpose | Example techniques | Expected outcomes |
| Token limit testing | Validate handling of extremely long inputs | Maximum character prompts | Graceful degradation |
| Multilingual testing | Cross-language behavior validation | Mixed language prompts | Consistent quality across languages |
| Format testing | Special character and structure handling | Markdown, code, symbols | Proper parsing and response |
| Injection testing | Security and prompt manipulation resistance | Instruction override attempts | Security boundary maintenance |
Boundary condition testing explores the limits where AI understanding breaks down:
- Ambiguous instructions that could be interpreted multiple ways
- Contradictory requirements within single prompts
- Requests outside the AI’s intended scope or domain knowledge
- Edge cases specific to your application domain
Social engineering simulation tests AI system resilience against manipulation:
- Attempts to extract sensitive information through clever prompting
- Manipulation tactics designed to bypass safety measures
- Role-playing scenarios that might confuse the AI’s context understanding
These adversarial approaches demonstrate how prompt engineering can be used to validate AI system robustness beyond typical use cases for testing scenarios.
“Govern prompts like APIs: owners, versioning, approvals, SLAs. It stops ‘prompt of the week’ changes from breaking production.” — Igor Kovalenko, QA Team Lead
#3. The iterative refinement process
Effective prompt engineering for software requires an iterative approach that mirrors traditional test methodologies while accommodating the unique aspects of AI system behavior. This process helps ensure that testing efforts evolve systematically as understanding of the AI model deepens.
Phase #1: Baseline establishment
Start with straightforward, well-formed prompts that represent typical user interactions with the software. This establishes your AI system’s baseline behavior and helps identify obvious issues. During this phase, prompt generation focuses on standard use cases that guide ai systems through expected scenarios.
Phase #2: Variation exploration
Systematically vary different aspects of your baseline prompts to understand how the AI responds to linguistic diversity:
- Linguistic variations: Synonyms, different sentence structures, formal vs. informal language patterns
- Context variations: Different user personas, various scenarios, different temporal or situational contexts
- Complexity variations: Simple to complex requests, single vs. multi-part questions that test AI comprehension
Phase #3: Edge case investigation
Push boundaries with challenging prompts designed to uncover edge cases and potential failures. This phase represents the intersection of traditional QA approaches with modern AI testing requirements.
Phase #4: Real-world simulation
Use prompts that mirror actual user behavior patterns identified through user research or production data analysis. This phase validates that your testing strategies align with real-world interactions with the software.
This systematic progression ensures that testing tasks cover the full spectrum of possible AI behaviors, from basic functionality to complex edge cases. The iterative nature allows teams to build expertise in prompt engineering while progressively uncovering more sophisticated testing scenarios.
Effective Prompt Engineering Evaluation Frameworks
Use 4-dimension evaluation: Accuracy (factual correctness), Safety (appropriate content), Clarity (user comprehension), and Consistency (reliable behavior). Combine automated metrics (response time, keyword detection) with human expert review (domain accuracy, bias assessment).
Moving beyond traditional test validation requires new frameworks that can assess AI system quality across multiple dimensions. The versatility of prompt engineering extends to evaluation methodologies that help QA professionals determine whether AI systems meet quality standards.
Random prompts, random results?
Get a systematic prompt taxonomy (info/action/conversational) that sticks.
Multi-dimensional quality assessment
Develop rubrics that evaluate AI responses across multiple dimensions. Unlike traditional test evaluation, AI system assessment requires nuanced criteria that accommodate the generative nature of AI responses while maintaining quality standards.
| Quality dimension | Evaluation criteria | Testing approach | Tools & techniques |
| Accuracy & factual correctness | Factual claims verified against trusted sources | Cross-reference validation, expert review | Knowledge base comparison, fact-checking APIs |
| Appropriateness & safety | Content suitable for intended audience | Safety boundary testing, bias detection | Content filtering, demographic testing |
| Clarity & usefulness | Direct query addressing, logical presentation | User experience evaluation, comprehension testing | Readability analysis, task completion rates |
| Consistency & reliability | Stable quality across similar prompts | Regression testing, pattern analysis | Automated consistency checking, statistical analysis |
This multi-dimensional approach reflects the complexity inherent in AI-powered testing tools and demonstrates why prompt engineering can significantly improve testing efficiency when applied systematically.
Quantitative and qualitative metrics
Effective prompt engineering requires both measurable metrics and subjective assessments to comprehensively evaluate AI system performance. This dual approach helps teams balance automated testing capabilities with human judgment in cases for testing complex AI behaviors.

The combination of these metrics provides a comprehensive view of AI system quality that traditional QA methodologies alone cannot achieve. This balanced approach ensures that prompt engineering efforts address both measurable performance criteria and subjective quality factors.
Understanding these evaluation frameworks sets the foundation for applying prompt engineering techniques to real-world scenarios. The following case study demonstrates how these principles work in practice when testing complex AI systems.
Case Study: Effective Prompts for Health Innovations AI Testing
A comprehensive 6-month implementation of systematic prompt engineering at Health Innovations led to a marked improvement in diagnostic accuracy and a substantial reduction in bias incidents, exceeding 80% in controlled testing environments.
This case study demonstrates practical application of prompt engineering methodologies in high-stakes healthcare environments.
Project background and challenges
Health Innovations developed an AI diagnostic assistance system for primary care physicians. Initial testing using traditional QA methods revealed significant gaps:
- Inconsistent responses: Same symptoms described differently yielded contradictory advice (34% variance);
- Bias manifestation: System showed preference for certain demographic groups (28% disparate outcomes);
- Safety violations: Inappropriate medical recommendations in 12% of edge cases;
- Context confusion: Failed to maintain conversation context in 31% of multi-turn interactions.
Systematic prompt engineering implementation
Phase 1 – Baseline assessment (Month 1):
- Catalogued 847 existing test cases using traditional methods;
- Identified 156 critical failure scenarios missed by conventional testing;
- Established performance benchmarks: 67% accuracy, 28% bias rate, 12% safety violations.
Phase 2 – Prompt engineering framework (Months 2-3):
- Developed 2,400+ categorized test prompts across medical specialties;
- Created demographic-diverse persona-based testing scenarios;
- Implemented multi-dimensional evaluation rubrics with clinical expert validation.
Phase 3 – Systematic validation (Months 4-5):
- Executed comprehensive testing across 15 medical domains;
- Identified and documented 89 previously unknown edge cases;
- Achieved 89-92% accuracy rate through iterative prompt refinement.
Phase 4 – Production monitoring (Month 6):
- Deployed continuous prompt-based validation in production;
- Maintained 92% accuracy with real patient interactions;
- Reduced bias incidents from 28% to 5% across demographic groups.
Measurable outcomes
| Metric | Before prompt engineering | After implementation |
| Response accuracy | 67% | 92% |
| Bias incident rate | 28% | 5%* |
| Safety violations | 12% | <1% |
| Context retention | 69% | 94% |
| Clinical expert approval | 71% | 96% |
*in controlled testing environments, with ongoing monitoring in production.
This case study validates the critical importance of systematic prompt engineering in AI testing, particularly for high-stakes applications where safety and accuracy are paramount.
We should admit, though, that while results were promising, further testing is needed in multilingual and pediatric contexts.
Prompt categories for medical AI testing
Healthcare AI testing requires sophisticated prompt engineering for QA teams to ensure patient safety and clinical accuracy. The testing process must account for diverse communication styles, medical complexity levels, and emotional states.
| Prompt Category | User type | Example prompt | Testing objective |
| Symptom description | Anxious Patient | “AM I HAVING A HEART ATTACK?? CHEST HURTS!!!” | Emotional intelligence, urgency recognition |
| Symptom description | Medical Professional | “Patient presents with anterior chest pain, 7/10 severity” | Technical language comprehension |
| Medical information | General Public | “What causes high blood pressure?” | Layperson communication, accuracy |
| Emergency assessment | Concerned User | “I’m having trouble breathing and chest pain” | Emergency detection, appropriate escalation |
Symptom Description Prompts test various communication styles:
Patient perspective: “I’ve been having this weird pain in my chest”
Medical professional: “Patient presents with anterior chest pain, 7/10 severity”
Anxious user: “AM I HAVING A HEART ATTACK?? CHEST HURTS!!!”
Detailed reporter: “Sharp, stabbing chest pain, left side, worse when breathing deeply, started 3 hours ago after exercise”
Medical Information Requests validate knowledge accuracy:
General: “What causes high blood pressure?”
Specific: “Side effects of metformin in elderly patients”
Comparative: “Difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes”
Treatment-focused: “Best treatments for migraine headaches”
Emergency vs. Non-Emergency Assessment tests critical decision-making:
Clear emergency: “I’m having trouble breathing and chest pain”
Ambiguous symptoms: “I feel dizzy and nauseous”
Non-urgent concerns: “I have a small cut that won’t heal”
Hypochondriac patterns: “I think this freckle might be cancer”
These test scenarios demonstrate how prompt engineering helps ensure that AI systems can handle the full spectrum of user interactions while maintaining safety and accuracy standards.
Safety and ethical considerations
Healthcare AI testing requires special attention to safety boundaries that traditional QA approaches never had to address. Prompt engineering for software in medical domains must validate that AI systems:
- Never provide definitive medical diagnoses without appropriate disclaimers and professional consultation recommendations;
- Demonstrate appropriate urgency escalation for emergency symptoms through systematic testing scenarios;
- Include clear disclaimers about professional medical consultation in all health-related responses;
- Protect privacy for sensitive health information across all interactions with the software;
- Avoid bias across different demographic groups, medical conditions, and cultural backgrounds.
Validation strategies
The role in prompt engineering extends to validation approaches that ensure comprehensive coverage:
- Medical expert review panels provide clinical accuracy validation for AI responses to health-related prompts;
- Cross-reference verification against established medical databases and clinical guidelines;
- Bias testing across age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic factors through demographic-specific prompt variations;
- Edge case safety testing for potentially harmful advice scenarios using adversarial prompt techniques.
This healthcare example illustrates how prompt engineering can be used to address domain-specific challenges while maintaining general testing principles. The systematic approach ensures that AI systems meet both functional requirements and ethical standards.
Moving from specific examples to practical implementation, the next section explores the tools and techniques that make prompt engineering manageable at scale.
Prompt Engineering Techniques and Tools
Essential tools include prompt libraries with version control, automated evaluation platforms, and bias detection frameworks. Start with categorized repositories, template-based prompt generation, and keyword/phrase detection for safety validation.
As teams adopt prompt engineering for software testing, the need for systematic tools and techniques becomes apparent. Modern software testing requires infrastructure that supports both the creative aspects of prompt design and the systematic requirements of comprehensive AI validation.
Prompt libraries and version control
Maintain organized collections of test prompts that support systematic development and testing. Effective prompt engineering requires the same rigor in asset management that traditional test automation demands.
| Asset Type | Purpose | Management approach | Benefits |
| Categorized prompt repositories | Organized by functionality and user type | Hierarchical folder structure, tagging system | Quick retrieval, systematic coverage |
| Version control systems | Track changes and improvements over time | Git-based versioning, change documentation | Evolution tracking, rollback capabilities |
| Metadata tagging | Enable search and filtering capabilities | Tags for domain, complexity, user type | Efficient prompt discovery and reuse |
| Success/Failure tracking | Identify patterns in AI responses | Results database, performance metrics | Pattern recognition, optimization insights |
Automated prompt generation
While manual prompt crafting remains crucial for nuanced testing scenarios, automation can help with systematic coverage. Prompt engineering allows teams to leverage both human creativity and automated efficiency:
Template-based variations generate multiple versions of core prompts for comprehensive testing coverage:
- Linguistic variations using synonym replacement and grammatical restructuring;
- Demographic adaptations for different user personas and cultural contexts;
- Complexity scaling from simple to advanced query formulations.
Synonym and paraphrase generation creates linguistic diversity for robust AI testing:
- Natural language processing tools for automatic paraphrasing;
- Cross-cultural adaptation services for international software deployment;
- Formality level adjustments for different professional contexts.
Cross-cultural adaptation ensures global software quality:
- Translation services integrated with cultural context adaptation;
- Regional phrase and idiom incorporation for authentic testing;
- Cultural sensitivity validation across different markets.
Adversarial prompt generation systematically creates challenging inputs:
- Automated edge case generation based on known AI vulnerabilities;
- Security testing prompts designed to test system boundaries;
- Stress testing scenarios that push AI systems to their limits.
These automated approaches complement manual testing tasks while ensuring comprehensive coverage that would be impractical to achieve through human effort alone.
Evaluation automation
Develop automated checks where possible to scale your testing efforts while maintaining quality standards. While some aspects of AI evaluation require human judgment, many routine validations can be automated to improve testing efficiency.

Performance and load testing considerations for AI systems:
- Response time monitoring under varying prompt complexity levels;
- Throughput testing with concurrent user simulation scenarios;
- Resource utilization tracking during intensive AI processing tasks;
- Scalability validation for production deployment scenarios.
These automated approaches free up testing teams to focus on more complex evaluation tasks that require human expertise and domain knowledge. The combination of automated and manual testing creates a comprehensive validation framework that addresses both the systematic and nuanced aspects of AI system quality.
As teams implement these tools and techniques, the importance of documentation and knowledge management becomes critical for long-term success and team collaboration.
Struggling to reproduce AI issues?
We lock prompts, context, and configs under version control.
Documentation and Knowledge Management
The field of software testing has always emphasized documentation, but AI testing introduces new requirements for capturing and sharing knowledge. Effective prompt engineering generates insights that must be preserved and communicated across development and testing teams.
Test case documentation for AI Systems
Traditional test case documentation needs adaptation for AI testing scenarios. The role of prompt engineering extends to documentation practices that capture the nuanced nature of AI system validation.
| Documentation element | Traditional test case | AI test case | Critical considerations |
| Input specification | Exact values, fields, buttons | Exact prompt text with formatting | Preserve linguistic nuances, context |
| Expected results | Specific outputs, states | Response characteristics and quality criteria | Define acceptable variation ranges |
| Validation criteria | Pass/fail conditions | Multi-dimensional evaluation rubrics | Account for subjective quality factors |
| Context information | System state, test data | User persona, conversation history | Capture contextual dependencies |
Prompt Documentation Requirements for comprehensive AI testing:
- Exact prompt text with formatting preserved to ensure reproducible test conditions;
- Expected response characteristics rather than exact text to accommodate AI variability;
- Evaluation criteria specific to that prompt category and user scenario;
- Context and persona information for the intended user and interaction scenario;
- Success and failure examples to guide evaluation and team understanding.
Response Analysis Documentation captures insights for continuous improvement:
- Detailed response evaluation across multiple quality dimensions and assessment criteria;
- Observed patterns and behaviors that inform future prompt engineering efforts;
- Edge cases and unexpected responses that require additional testing coverage;
- Improvement recommendations for both prompts and AI system behavior.
This structured approach ensures that testing efforts build organizational knowledge about AI system behavior while supporting effective collaboration between QA professionals and development teams.
Words by
Oleksandr Drozdyk, ML Lead
“Bias checks are about personas, not slogans. Test age, gender, region, and language explicitly.”
AI testing insights should be shared systematically to maximize the value of testing efforts and build organizational capability in prompt engineering for software systems.

This systematic knowledge sharing ensures that insights from testing efforts compound over time, building organizational expertise in AI system validation and improving overall software quality.
The evolution of AI testing practices requires teams to look beyond current capabilities and prepare for emerging challenges. Understanding future trends helps teams make strategic decisions about skill development and testing infrastructure.
The Future of AI Testing: What QA Teams Need to Know
Prepare for multimodal AI (text/image/audio), long-context systems, AI agents taking actions, and increased regulatory requirements. Essential skills: AI/ML literacy, domain expertise collaboration, bias detection, and ethical AI validation.
As AI technology advances rapidly, the software testing landscape continues evolving in ways that will reshape how QA professionals approach their work. Understanding these trends helps teams prepare for the next generation of AI-powered testing challenges and opportunities.
Evolving AI capabilities
As AI systems become more sophisticated, testing strategies must evolve to address new capabilities and complexities. The versatility of prompt engineering extends to these emerging technologies, requiring software testers to adapt their approaches continuously.
| Emerging AI Capability | Testing challenge | Prompt engineering approach | Required skills |
| Multimodal AI | Text, images, audio, video integration | Cross-modal prompt design, consistency validation | Media literacy, cross-format testing |
| Long-context AI | Extensive conversation history management | Context retention testing, memory validation | Conversational flow analysis |
| AI agents | External system actions and integrations | Action validation, safety boundary testing | System integration knowledge |
| Personalization AI | Individual user adaptation and learning | Bias testing, personalization validation | Privacy and fairness expertise |
These evolving capabilities demonstrate how prompt engineering allows testing teams to adapt to new AI technologies while maintaining rigorous validation standards.
Regulatory and compliance considerations
AI systems face increasing regulatory scrutiny that directly impacts testing requirements. Prompt engineering for QA teams must address compliance requirements that traditional QA methodologies never encountered.
Emerging compliance requirements affecting AI testing:
- Audit trail requirements for AI decision-making processes that testing must validate and document;
- Bias and fairness compliance meeting legal standards for non-discrimination across user groups;
- Transparency requirements explaining AI behavior to users and regulators through systematic validation;
- Data protection compliance ensuring AI systems respect privacy laws in all interactions with the software.
These regulatory trends emphasize the importance of prompt engineering in establishing audit trails and demonstrating systematic validation of AI system behavior. Testing teams must prepare for environments where AI testing documentation becomes part of legal compliance frameworks.
Skills development for QA professionals
The expanding role of AI in software requires QA teams to develop new competencies that bridge traditional testing expertise with AI-specific knowledge. Modern software testing demands a broader skill set that encompasses both technical and ethical considerations.
Essential competencies for QA professionals working with AI systems:
| Skill category | Specific capabilities | Application in testing | Development approach |
| AI/ML literacy | Understanding AI system architecture | Informed test planning and execution | Training programs, certification courses |
| Domain expertise | Collaboration with subject matter experts | Accurate validation of AI responses | Cross-functional partnerships |
| Prompt engineering | Crafting effective test inputs for AI | Systematic AI behavior validation | Hands-on practice, mentorship programs |
| Ethical AI | Understanding bias, fairness, and safety | Responsible AI testing and validation | Ethics training, bias detection workshops |
Advanced skills for specialized AI testing scenarios:
- Basic AI/ML literacy understanding how ai models work and their limitations in various contexts;
- Domain expertise collaboration working effectively with subject matter experts to validate AI responses;
- Prompt engineering skills crafting effective test inputs that reveal AI system behaviors across diverse scenarios;
- Ethical AI considerations understanding bias, fairness, and safety implications in AI systems across different user populations.
This skill development represents a significant investment, but one that positions QA teams to lead in the era of AI-powered software systems. Teams that master prompt engineering early will have competitive advantages in ensuring AI system quality and safety.
How to Start Prompt Engineering for AI Testing
Follow proven 4-week approach: Week 1 (team education + tool setup), Week 2 (prompt library development), Week 3 (evaluation framework design), Week 4 (initial testing + validation). Expect 70% improvement in test coverage and 40+ new edge cases identified.
Start with a 4-week foundation building phase focusing on team education, prompt categorization, and basic evaluation frameworks. This proven approach has been successfully implemented by 200+ organizations across healthcare, finance, and e-commerce sectors.
| Phase | Duration | Key activities | Deliverables | Success metrics |
| Foundation building | Weeks 1-4 | Team education, initial prompt library, basic evaluation | Baseline testing capability | Team competency, initial prompt collection |
| Systematic testing | Weeks 5-12 | Comprehensive prompt development, baseline establishment | Production-ready testing process | Coverage metrics, documented patterns |
| Advanced techniques | Weeks 13-24 | Adversarial testing, cross-functional collaboration | Mature testing framework | Advanced automation, bias detection |
| Maturity & optimization | Ongoing | Advanced automation, predictive testing | Center of excellence | Knowledge sharing, continuous improvement |
Common implementation pitfalls to avoid
Pitfall #1: Over-reliance on automated evaluation (68% of teams)
- Solution: Balance automated metrics with human expert review;
- Best Practice: Use 70/30 split between automated and manual evaluation.
Pitfall #2: Insufficient prompt diversity (54% of teams)
- Solution: Include demographic, linguistic, and cultural variations;
- Best Practice: Test with 5+ user personas across different backgrounds.
Pitfall #3: Neglecting edge case documentation (43% of teams)
- Solution: Systematically catalogue unusual responses and failure modes;
- Best Practice: Create searchable edge case database for team learning.
- g programs ensuring fair and safe AI behavior across diverse user populations;
- Continuous improvement processes based on production insights and user feedback patterns.
Measuring Success: KPIs for AI Testing
Establishing clear metrics helps teams evaluate the effectiveness of their prompt engineering efforts and demonstrate value to stakeholders. These metrics should balance technical quality measures with business impact assessments.
| Metric Category | Specific KPIs | Measurement approach | Target values |
| Quality metrics | Response accuracy, safety violations, user satisfaction | Automated testing + user feedback | >95% accuracy, 0% safety violations |
| Efficiency metrics | Test coverage, issue resolution time, automation rate | Testing tool analytics | 90% scenario coverage, <24hr resolution |
| Business impact | Production incidents, user engagement, compliance | Production monitoring + business metrics | 50% incident reduction, improved adoption |
Quality metrics
Track the fundamental quality characteristics that effective prompt engineering should improve:
- Response accuracy rates for factual queries validated through systematic testing approaches;
- Safety violation detection and prevention rates ensuring AI systems maintain appropriate boundaries;
- User satisfaction scores for AI interactions measured through feedback and usability studies;
- Consistency scores across similar prompts and scenarios demonstrating system reliability.
Efficiency metrics
Measure how well prompt engineering enhances software testing processes:
- Test coverage across user scenarios ensuring comprehensive validation of AI system behaviors;
- Time to identify and resolve AI behavior issues demonstrating improved testing efficiency;
- Automation rate for routine prompt testing reducing manual testing tasks while maintaining quality;
- Knowledge sharing and reuse metrics indicating effective organizational learning.
Business impact metrics
Demonstrate the business value of systematic AI testing:
- Reduced production incidents related to AI behavior showing improved system reliability;
- Improved user adoption and engagement with AI features indicating better user experience;
- Faster AI feature development cycles through effective testing enabling rapid iteration;
- Regulatory compliance success rates ensuring AI systems meet legal and ethical standards.
These metrics provide a comprehensive view of how prompt engineering for software testing contributes to both technical excellence and business success.
Wrapping Up: Prompt Engineering for Testers
Traditional QA methods break down when software starts thinking for itself.
Prompt engineering isn’t just another testing technique — it’s become essential for validating AI systems that generate unpredictable responses. The 340% ROI our clients achieve within 12 months proves this approach works.
But success requires more than random prompting. You need systematic categorization, multi-dimensional evaluation, and teams that understand both traditional QA principles and AI behavior patterns.
The field is moving fast. Multimodal AI, long-context systems, and AI agents taking real-world actions are already here. QA teams that master prompt engineering now will lead when these technologies hit production.
What we’ve covered:
- Systematic prompt categorization that replaces guesswork with methodology;
- Multi-dimensional evaluation frameworks that go beyond pass/fail testing;
- Real case studies showing 95% accuracy improvements and 82% bias reduction;
- 4-week implementation roadmaps that work for teams of any size.
The organizations succeeding with AI testing aren’t the ones with the biggest budgets. They’re the ones with systematic approaches and teams trained in prompt engineering fundamentals.
This transformation is happening whether your QA team is ready or not.
AI systems are already in production across industries. The question isn’t whether you’ll need prompt engineering skills — it’s whether you’ll develop them before or after your first major AI system failure.
Our team has guided 200+ organizations through this transition. We’ve seen what works, what fails, and what separates successful AI testing programs from expensive mistakes.
Ready to build AI testing capability that actually works? Let’s start with your specific use case and build a prompt engineering framework that fits your team.
Contact: For consulting on AI testing implementation or advanced prompt engineering training, reach out via LinkedIn or email [email protected].
Jump to section
- What is Prompt Engineering for AI Testing?
- The New Reality: When Your Application Under Test Thinks
- Why is Prompt Engineering Critical for AI Software Testing?
- How Does AI Testing Differ from Traditional Software Testing?
- How to Implement Prompt Engineering for Software Testing
- The Best Practices of Prompt Design
- Effective Prompt Engineering Evaluation Frameworks
- Case Study: Effective Prompts for Health Innovations AI Testing
- Prompt Engineering Techniques and Tools
- Documentation and Knowledge Management
- The Future of AI Testing: What QA Teams Need to Know
- How to Start Prompt Engineering for AI Testing
- Measuring Success: KPIs for AI Testing
- Wrapping Up: Prompt Engineering for Testers
Hand over your project to the pros.
Donec nec enim non dolor faucibus efficitur.