Did you know that 70% of projects fall short of meeting their targets, while the cost of overall failures caused by poor-quality software has reached a staggering $1.56 trillion? These numbers might seem surreal given the cutthroat competition in the world of software development, but they are true. Many companies still underestimate the importance of testing, putting the success of their products and services at risk. Do not take the leaf from these companies’ books.
Testing is a crucial part of software development that determines the success of development projects. And, sooner or later, every software owner will need to ponder over the testing strategy. It’s not a question of “if”, but “when”. Even if you don’t have the means or the real need to hire an in-house team of testers, there are at least a couple of solutions — one of them is to outsource testing to a remote QA testing company, and another one is to use testing as a service (TaaS).
So, what is TaaS? How is it different from the traditional QA service? And is it the best route for you? In this guide, we’ll answer these questions in detail while sharing some practical tips on implementing it in your business. Let’s start digging.
Key Takeaways
- Quality Assurance as a Service is a testing model that allows businesses to access high-quality testing services without the need to hire and maintain an in-house QA team.
- One of the benefits of QA as a Service is cost efficiency. Compared to the traditional model, where you need to invest in hiring, training, and maintaining full-time QA staff, you have no extra expenses, allowing you to save up to 20% on costs.
- With QA as a Service, businesses can grow at their own pace, scaling their testing efforts up or down depending on the current project needs.
- QAaaS perfectly works with agile methodologies, allowing teams to integrate it throughout the entire development lifecycle.
- QAaaS includes a wide range of testing services, such as functional, automation, performance, security, and exploratory testing, making it a perfect fit for businesses looking to cover all aspects of QA.
- Hiring third-party testers to run tests for your business helps significantly speed up the SDLC. QA engineers can step in at any stage of the development process and make sure the product you build is thoroughly vetted for bugs.
- The key benefit of QAaaS is its versatility. Ideal for startups with limited resources, it perfectly suits large companies as well, offering them an easy way to expand their testing capabilities without long-term commitments.
What Is QA Testing as a Service?
Testing as a service, also known as QA-managed services or on-demand testing, is a model of testing performed by a third-party vendor. Just like traditional testing services, TaaS pursues the goal of ensuring that quality is built into a product or service and meets customers’ requirements.
However, traditional testing and testing as a service aren’t the same thing. The main difference between the two lies in the pricing model structure. In the case of an in-house team, you’d be paying testers their rates. For example, if you have 5-8 testers on the team, you’ll be charged their monthly rates accordingly. In regard to the QA testing as a service, you’ll pay for the work you’ve used.
So, unlike traditional QA testing, testing as a service isn’t about hiring people; it’s about receiving the service and paying for the outputs delivered by the service provider.
Check out our test cases on software testing to see how we can help you
Why Has Quality as a Service Emerged?
You might be wondering why this testing approach has emerged in the first place. Well, there are a number of reasons.
First and foremost, software applications have become more sophisticated and complex. Nowadays, applications integrate various technologies and need to function seamlessly on multiple platforms, making it challenging for most testing methods to keep up with the pace.
Then there’s the rise of agile. With agile methodologies becoming widely adopted worldwide, introducing a more flexible approach to testing has become necessary to ensure that businesses can continuously test their products or services, moving beyond the rigid confines of the traditional testing lifecycle.
Aside from that, QA testing as a service offers a cost-effective solution by allowing companies to outsource their testing needs without the overheads of hiring, training, and maintaining a dedicated team. To give you an idea, according to Opinov8, using testing as a service model can lead to cost savings of up to 20%, which isn’t a small feat.
No less important is the fact that this method allows businesses to tap into the specialized testing expertise they need and launch truly groundbreaking products. Unlike most in-house QA teams, often limited in resources, TaaS providers are equipped with the advanced tools necessary to thoroughly test software products and services in a wide range of areas, from security to automation.
Last but not least, the reason this service has become so popular is because of the flexibility and scalability it offers. Since businesses aren’t tied into long-term commitments, they can outsource testing as needed to adapt to changing requirements. For software development, where demands change frequently, this is an important advantage.
How Does QA as a Service Model Work?
Let’s take a closer look at how QA as a service works to see if this model is the right fit for you. In general, the basic principle isn’t much different from traditional testing methods. It can be implemented early in the development lifecycle, tested throughout the software development process, used to validate the build of a specific prototype or to test just one feature of a larger project. By and large, the team has complete control over the testing scope.
When it comes to the choice of vendor, QAaaS can be either outsourced (via a third-party provider) or crowdsourced (via a community of independent testers), depending on the specific testing needs of your business. Both types have advantages in terms of cost, expertise, and scalability, which we’ll discuss later in the article.
The strength of QAaaS is that the team in this model is more flexible and adaptive to changes than a traditional testing team. Essentially, you get a group of people with different testing backgrounds and extensive hands-on experience in various industries and technologies. These people bring a diverse range of insights and innovative approaches to the testing process and bug detection. Testing itself is performed via cloud-based tools and platforms, making it easy to scale up and down testing resources based on your business’s current needs.
Speaking of quality assurance engineers, they don’t just do testing. Instead, they advocate for product quality, ensuring all possible test cases and scenarios have been factored in. As for the testing capabilities and scenarios, they are broader and more flexible. Because there’s a greater number of testers involved, the most vulnerable areas of the project are paid extra attention and retested by users in real-world environments at the same time. All in all, crowdsourcing is about bringing a large number of independent testers and having their feedback analyzed by a central platform or service.
In case outsourcing is involved, a quality assurance provider is represented by a company that offers testing solutions and QA services to other companies as a cloud-based service. All software needs are outsourced to a third-party vendor who offers various testing approaches as well as tools and frameworks, saving time and resources on technology and training.
Types of Quality Assurance As a Service
As mentioned earlier, QA as a service is a rather broad approach that isn’t limited to a particular phase of the software development life cycle. It can be implemented effectively early in the process as well as in the post-production phase. In addition, it covers a number of different types of QA as a service, including but not limited to:
- Functional testing — the most basic form of testing performed to ensure that software’s functionality operates as expected. Most often, it’s run in the early stages of development.
- Test automation — a type of testing that allows repetitive but necessary checks to be performed efficiently. Automated testing proves particularly useful for large projects with frequent updates, as it helps maintain consistency and speed in the testing process.
- Performance testing — this involves testing the software’s performance under various conditions, including load, stress, and scalability.
- Security testing — it helps uncover vulnerabilities in the software that could lead to data breaches or other security incidents.
- Usability testing — a specific type of functional testing focused on the user’s experience.
- Compatibility testing — it helps ensure that the software works across different devices, OS, and browsers without compromising functionality.
- Regression testing — this type of testing is conducted to ensure that new changes haven’t adversely affected existing functionalities.
- Disaster recovery testing — a form of testing used to validate the software’s ability to recover from incidents if they occur.
- Exploratory testing — when traditional testing techniques don’t suffice, QA teams resort to exploratory testing, allowing them to identify defects that may not have been caught by structured testing methods.
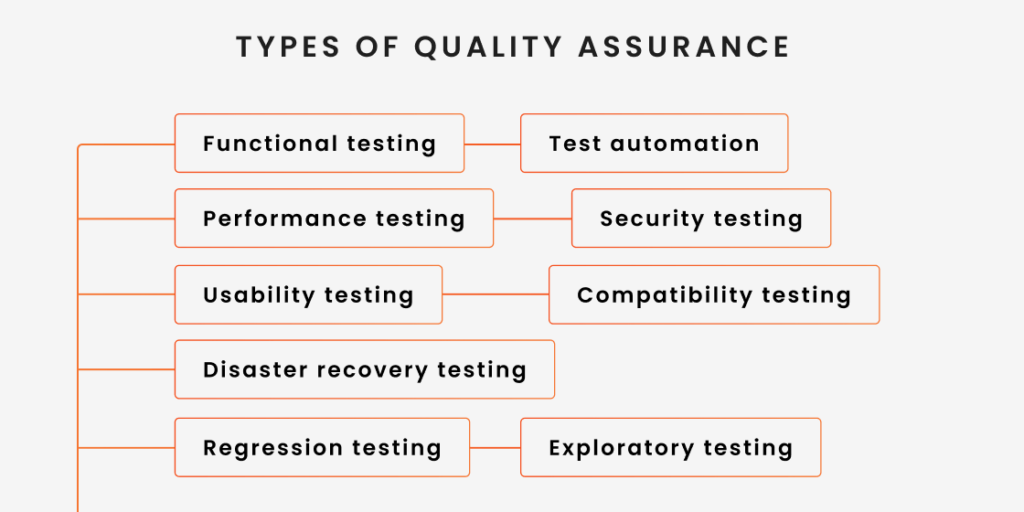
Each of these types is important in the overall quality assurance process, enabling QA teams to get an idea if the software’s robust, reliable, and ready for deployment. The best thing is QA as a Service allows businesses to access any of these types of testing without the need for extensive in-house resources and align their software development with the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Whether you need help with testing a new feature or an entire project from scratch, we’ve got you covered
Why Testing as a Service Is a Game-Changer for Businesses
Testing is quite expensive. In fact, it’s just a fraction cheaper than development, significantly driving the final cost of the software product up. In Eastern Europe, the average hourly rate of a QA tester starts from $18, while in the US, the rate of the same tester can be $50 and higher, depending on the skills and experience. Now, considering that testing takes about 20% of the entire timeline of the SLDC, you can get a rough estimate of the cost. No wonder many small companies leave testing to developers in the hope of curtailing operational costs.
However, this isn’t the right way to go. First, this doesn’t help in terms of speed. People don’t easily notice defects in the products they’ve created themselves. And second, the quality of testing can be compromised. It’s not us who said that testing must be carried out by unbiased experts, but we couldn’t agree with that more. Only by letting external experts test your product can you hope to polish software quality and produce something groundbreaking.
Benefits of QA as a Service
Let’s consider the primary benefits of using QA services for a business.
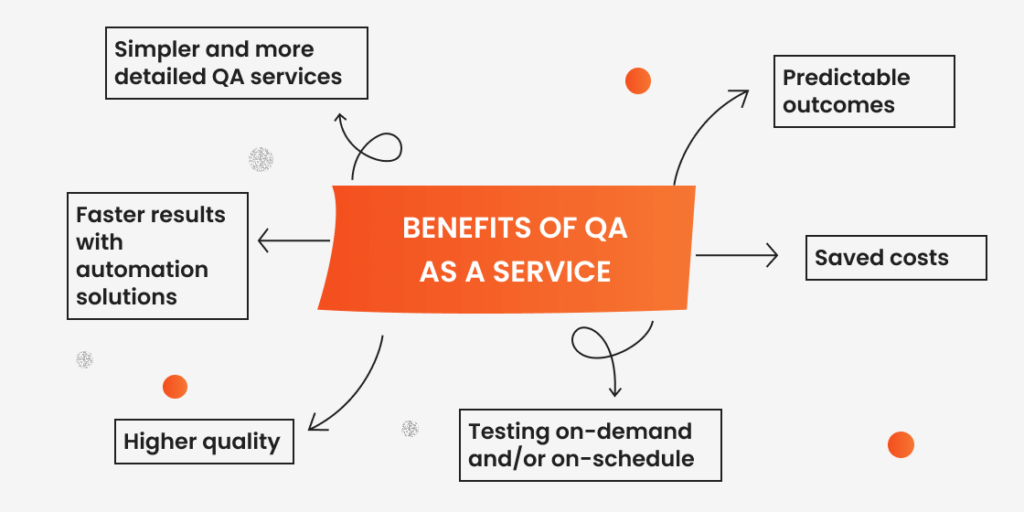
Simpler and more detailed QA services
New technologies and app enhancements can be adopted faster with QAaaS. There is a sense of urgency. The team that is participating in the process is experienced and proficient enough to go straight into the specifics of a given project. The basics can be skipped. QAaaS provides access to the most recent testing tools and technologies, which improve testing efficiency and effectiveness.
Higher quality
Since a software quality assurance service provider has extensive experience delivering testing services in many industries for various clients, the level of quality of QA procedures is improved. Instead of adopting superior technologies and approaches on your own, you produce better software by incorporating quality assurance as a service team into the process. At a reasonable cost, you can build better software while substantially boosting efficiency. New people in a team with good expertise in the area can add fresh perspectives and ideas to the entire testing process.
Faster results with automation solutions
If you provide automation solutions to match sprint cycles and speed up the process, you may accumulate your team’s resources elsewhere, where they might be needed. It is an efficient method to reduce time-to-market.
Testing on-demand and/or on-schedule
Unlike managing a team of testers in-house, testing as a service allows you to use testing servers as and when required by the process. Ultimately, this helps with better planning and resource allocation and reduces the risk of idle periods or unnecessary delays.
Predictable outcomes
QA as a Service provides businesses with a sense of security and reliability in their software development, which is crucial for maintaining the software and updates. Furthermore, the expertise of QA teams also greatly reduces the risk of defects, allowing companies to build software products that are bug-free, stable, and reliable. More importantly, testing as a service brings more clarity into the timeline of the development cycle. As a result, it’s easier to make estimations and meet project deadlines.
Saved costs
The ability to attract an outsourced team as needed during the project eliminates the necessity to maintain a large testing team and infrastructure running on a daily basis. The process is more customized in accordance with the original budget and requirements. In quality assurance as a service, you pay for the actual outcomes, which are newly discovered defects, rather than the hours invested in teamwork.
Not sure if TaaS is the service you need? Share with us your product’s details, and we’ll help you make the right decision!
Do You Need TaaS for Your Business?
In most cases, testing as a service is a fail-safe choice for most firms, including those that aren’t related to software development. It helps improve the product’s quality and detect vulnerabilities, preventing them from slipping into later stages when the product is ready to be launched.
Here are the main use cases for QA as a service:
- Tech startups with limited resources. If you’ve recently started out and lack the in-house team of testers to conduct testing, TaaS can be a great solution. It provides access to a wide range of testing tools and expertise without the need for significant upfront investment.
- Large companies. You may want to resort to TaaS to expand your testing coverage while freeing up in-house testers’ time to focus on other strategically important tasks.
- Mobile developers. Given the diversity of mobile devices and operating systems, mobile app developers benefit from testing as a service to ensure their applications perform well across all platforms.
- Businesses from other industries like e-commerce, healthcare, fintech, and so on. Any other industry with a digital product dealing with sensitive data can benefit from comprehensive testing offered by TaaS.
- Businesses that undergo digital transformation. Companies transitioning to digital platforms need thorough testing to ensure their new systems are reliable, user-friendly, and secure.
When Quality Assurance as a Service May Not Be Needed
Despite the many benefits offered by testing as a service, their use may be an overkill for small companies that have standard IT solutions and minimal customization or run in-house testing teams. In most cases, they’d be quite happy with simpler, traditional testing methods and won’t consider outsourcing. Aside from that, testing as a service isn’t very popular among businesses that do not have frequent software updates. Since they don’t need continuous testing, they often find it more cost-effective to manage testing internally.
How to Integrate Quality Assurance in Your Business
If you believe that your business can benefit from TaaS and are looking for tips to implement it into your workflow, our recommendations may come in handy. Read on to find out what steps are required to make your integration a success.
Assess Your Needs
While this might seem pretty basic, the first step is to look into your testing processes and pinpoint areas for improvement. Are there certain types of testing that your team struggles with? Do you find it challenging to keep up with testing during peak development periods? Or maybe you lack the expertise to test certain advanced features? Don’t rush here. Take your time to understand the gaps and determine if — and how — testing as service can serve your needs.
Choose the Right Provider
The next step is to find a service provider. This isn’t always easy, as no providers are created equal, even though they all claim to be good. To sift through an array of all available options, make sure to start by reading other clients’ reviews. This will help you get an idea of what domains they are the most proficient in and how well they did the job.
Many testing-as-a-service providers lure clients with low price tags. However, make sure not to fall for this too quickly. Often, these low prices come with significant trade-offs, such as a shortage of qualified testers and inadequate testing coverage, making the savings not worth it.
We’d also advise paying attention to the provider’s approach to communication because poor project management can kill even the most promising testing endeavors. Choose a QA service provider that prioritizes effective communication and is quick to respond. You may have any kind of issues as you proceed with development, and it’s crucial that a company that provides QA can resolve them on the spot.
We have 250+ physical devices, enabling us to provide our clients with extensive testing coverage
Set Clear Goals
After selecting a vendor, be sure to talk with them about your specific needs and what you expect from their services. At this step, it’s important to provide them with as much information about your project as possible to prevent any surprises or unforeseen costs down the line. Ideally, you should also give them the performance metrics that are important to you and establish a desired timeline.
Stay on Track of the Progress
Of course, handing over a project to a QA service provider doesn’t mean you should step back completely. Regular monitoring and engagement are key to ensuring that testing is carried out in line with your project goals. Establish a system of regular updates and checkpoints. These could be, for example, progress reports or real-time dashboards, whichever suits you best. By tracking the progress of testing, you’ll not only ensure that you’re moving in the right direction, but you will also quickly resolve any issues quickly and keep your project on track.
Besides everything we said above, we’d also like to highlight the importance of protecting your intellectual property. If you don’t want months of work you’ve put into the project to be spent in vain, make sure to include NDAs and other legal safeguards in the agreement with your provider to protect your assets.
Final Thoughts
To bring it to an end, testing as a service offers plenty of benefits, making it a viable option for businesses across various domains. The most important one is that it can be scheduled on demand, enabling you to test products or services only when necessary. This flexibility makes it possible to scale testing efforts up and down without the need to make a commitment, as in the case of in-house testing teams. Whether you’re a startup limited in resources or a large company looking to expand your testing coverage, software testing as a service can benefit you.
Jump to section
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!