Accessibility has been an increasingly widely discussed topic in the software community for the past few years, but right now, digital accessibility is finally becoming a legal and business priority, especially across the European Union. The trigger for the change is the European Accessibility Act, which has been the accessibility standard for years before finally becoming mandatory for businesses starting in June 2025.
As a result, many businesses are now facing concrete obligations to make their digital services usable for people with disabilities to avoid penalties, legal trouble, and reputational losses, as well as gain a significant competitive advantage. Let’s look at the key EAA requirements, who they apply to, and how to achieve compliance with the new rules.
What Is the European Accessibility Act?
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is an EU directive designed to make key products and services more accessible to people with disabilities. It promotes equal access to digital and physical environments, such as websites, mobile apps, ebooks, ticketing machines, and online banking.
The EAA marks a shift in accessibility from being a best practice to a legal requirement, at least within the EU. It also standardizes accessibility requirements across EU member states, simplifying compliance for businesses operating in multiple countries.
Although the act was primarily designed for individuals with disabilities, it also benefits older adults and anyone facing situational limitations, like using a phone in bright light or navigating a site with one hand. Ultimately, the EAA encourages more inclusive, user-friendly design across the board, and that is something that’s going to benefit customers even outside of the European Union and without disabilities that prevent them from fully accessing digital services.
From UI/UX design to testing — we will help you build strong, accessible, future-proof software
European Accessibility Act 2025 Deadline
The European Accessibility Act officially becomes enforceable on June 28, 2025. By this date, all businesses covered by the directive must ensure their products and services meet the required accessibility standards. The June 2025 deadline marks the end of the transition period granted after the EAA was adopted in 2019, giving organizations enough time to prepare and meet the accessibility standards outlined by the act.
With the enforcement date approaching, companies that haven’t started working toward meeting EAA standards face increasing risk. While some member states may have slightly different national implementations, the core obligations remain consistent across the EU. This means that the sooner you start getting proactive about meeting accessibility compliance requirements, the easier it will be for your business to remain competitive and risk-free in the EU market.
Businesses, Products and Services That EAA Applies To
The TL;DR version of this section is: If you provide services to customers across the European Union or your business has a digital presence in the region, then the European Accessibility Act compliance is mandatory for you. Still, let’s look at the types of businesses and services that need to comply with the EU accessibility regulations.
The European Accessibility Act applies primarily to businesses offering digital products and services to consumers within the EU. This includes both EU-based companies and non-EU providers targeting the European market. The directive focuses on consumer-facing services rather than internal systems, meaning that if your product or service is publicly available and used by end users, it likely falls under the EAA’s scope.
Digital products and services covered by the EAA include:
- Websites and mobile applications
- eCommerce platforms
- Banking services and ATMs
- Ticketing and travel check-in machines
- Telecommunications services and equipment
- Ebooks and electronic readers
- Media and streaming platforms

Who Can Be Exempt From Being Compliant?
While the European Accessibility Act applies broadly to businesses offering digital products and services in the EU, there are specific exemptions designed to reduce the burden on smaller organizations and account for practical limitations. This means that the rules of compliance may not apply to you specifically, but a little later in this article, we’ll cover why it’s still important to meet EAA compliance requirements even if you are technically exempt from them. Here are the types of organizations to which the rules of compliance with the European Accessibility Act may not apply.
Microenterprises
The EAA generally exempts microenterprises, which are defined as businesses with fewer than 10 employees and an annual turnover or balance sheet total of less than €2 million. These businesses are not required to comply with the act unless national legislation introduces additional requirements or the enterprise operates in a regulated sector like public services or finance.
Disproportionate burden clause
Even for businesses that are not exempt by size, the EAA allows for limited exceptions if compliance would impose a disproportionate burden. This applies in cases where making a product or service accessible is technically unfeasible or would cause significant financial hardship relative to the company’s resources. However, this must be justified with clear documentation, and authorities can review such claims to ensure that no accessibility barriers are put up for no reason.
Legacy products and services
In some cases, the EAA does not require retroactive changes to legacy products or services already on the market before the compliance deadline, unless they undergo significant updates. That said, updates and new releases after June 28, 2025, must meet common accessibility requirements.
Although some organizations may be exempt, it’s clear that aligning with EAA principles is still a strategic move. Accessibility improves user experience, opens new market segments, and helps future-proof products in an increasingly inclusive digital realm.
Not sure how to be EAA-compliant or where to start? We’ve got you covered!
What Happens If You Don’t Ensure Compliance With the EAA?
The need to meet accessibility standards in the EU is no longer a nice-to-have feature on top of a software or hardware solution — there are very real consequences of ignoring the rules for digital accessibility in the EU. Here is what businesses can face if they don’t follow the requirements of the European Accessibility Act.
Legal obligation under EU law
The European Accessibility Act introduces mandatory accessibility requirements for a wide range of digital products and services. For businesses that fall under its scope, compliance is not optional. After June 28, 2025, failure to meet the EAA standards can trigger enforcement actions across EU member states.
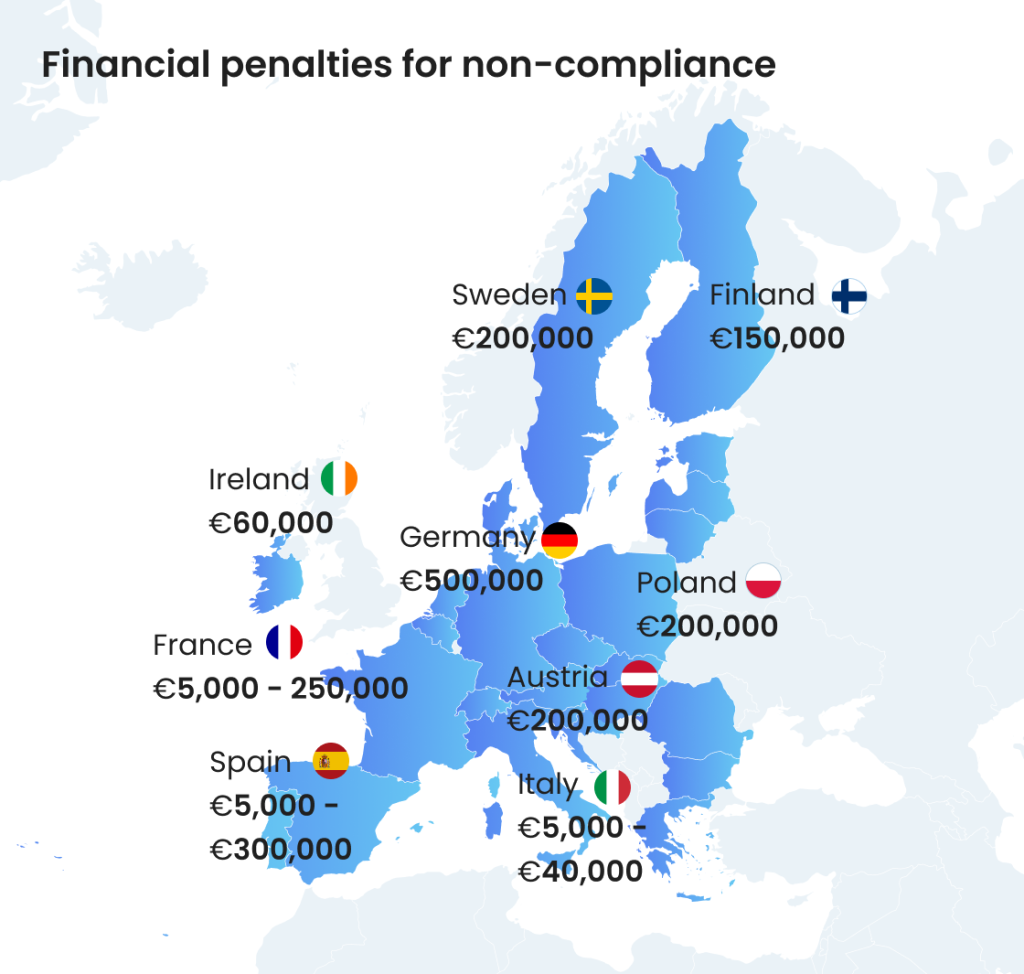
Financial penalties for non-compliance
Companies that don’t comply risk facing fines, sales restrictions, or orders to withdraw non-compliant products or services from the market. While exact penalties vary by country, most enforcement mechanisms include the power to impose administrative fines and corrective action. In severe cases, repeated non-compliance may result in product bans or service suspensions. This is just a taste of the fines companies can face in the case of being exposed for non-compliance:
- Germany: Fines up to €500,000 for serious violations.
- France: Fines from €5,000 to €250,000 for inaccessible platforms.
- Italy: Fines from €5,000 to €40,000; up to 5% of turnover for some entities.
- Spain: Fines up to €600,000 for very serious infractions.
- Sweden: Fines up to €200,000, plus mandatory corrective actions.
- Ireland: Fines up to €60,000 and/or imprisonment for non-compliance.
- Austria: Fines up to €80,000 based on severity.
- Netherlands: Fines up to €250,000; possible service suspensions.
- Poland: Fines up to €1,500 or 10% of annual turnover.
- Czech Republic: Fines up to €400,000 depending on business size and severity.
Risk of lawsuits and reputational damage
Beyond regulatory enforcement, businesses may also face lawsuits from consumers or advocacy groups. Legal action can lead to compensation claims and long-term damage to brand trust. In the digital economy of 2025, inaccessibility can quickly become a public issue, especially if it excludes people from accessing essential services like banking, eCommerce, or transportation.
Why Else EAA Compliance Matters
With an increased amount of attention paid to accessibility in the EU, the implementation of the EAA requirements and ensuring complete compliance unlocks more benefits than just reduced legal and financial risks. Here is why else you need to work on ensuring digital accessibility under the EAA regulations.
Access to a wider market
More than 101 million people in the EU, or 1 in 4 Europeans over the age of 16, live with some form of disability. Making digital services accessible allows businesses to both explore this underserved segment and demonstrate social responsibility. Accessibility also benefits aging users, people in temporary or situational limitations, and those using assistive technologies.
Improved usability for all
Accessible design often results in a better experience for everyone, not just those with disabilities. Features like keyboard navigation, clear content structure, compatibility with different devices and platforms, and consistent UI design enhance usability, reduce support requests, and increase customer satisfaction.
Lower long-term development and maintenance costs
Building accessibility into your design and development process, especially when paired with proper accessibility testing, reduces the risk of costly reworks later. It also simplifies compliance with future regulations and helps avoid disruptions during product updates or international expansion.
Key Requirements of the EU Accessibility Act
The European Accessibility Act establishes a unified set of accessibility requirements for digital products and services across the EU. It aims to ensure equal access for people with disabilities by requiring businesses to make their offerings accessible throughout the design, development, testing, and delivery phases. Let’s look at what ensuring full accessibility across your digital presence currently involves.
Functional accessibility requirements
The EAA does not prescribe specific technologies, instead focusing on functional outcomes. Core principles here include:
- Perceivability. Information must be presented in ways users can perceive (for example, using screen reader compatibility or text alternatives).
- Operability. Interfaces must work with keyboards and assistive technologies.
- Understandability. Content must be clear, consistent, and easy to follow.
- Robustness. Solutions must remain compatible with evolving technologies.
To meet these goals, accessibility experts encourage businesses to align with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, widely recognized as the benchmark for digital accessibility. While the EAA doesn’t explicitly mandate WCAG compliance, many member states are adopting it as the key technical standard for evaluating accessibility.
Accessible information and support
Beyond the interface itself, which mainly concerns application and website accessibility, businesses must also ensure:
- User instructions, help content, and support channels are accessible.
- Accessibility features are clearly documented and available in alternate formats if required.
Ensure a bright, risk-free future for your products with expert-level accessibility testing services
How to Comply With the EAA: The 5-Step Process
Ensuring the accessibility of products and services under the EAA may seem like a highly complex task. However, with the right approach and thoughtful planning, businesses can not only reactively get rid of many common accessibility issues, but actually build a culture of accessibility directly into their development process. Here are the five steps to help you follow accessibility standards across the EU digital market.
1. Assess your current accessibility status
Start by conducting a comprehensive accessibility audit of all relevant products and services, including websites, mobile apps, hardware interfaces, and documentation. This helps identify where you stand in relation to common accessibility standards such as WCAG 2.1 and EN 301 549. Look for barriers like missing alt text, poor keyboard navigation, low contrast, or unreadable PDFs. The goal is to understand your risk exposure and create a roadmap for remediation.
2. Understand what applies to you specifically
The EAA doesn’t apply to everything. Identify which of your products and services fall under its scope — this typically includes anything related to eCommerce, banking, telecom, transportation, media, and digital communication. Also, determine whether you qualify for an exemption (for example, if you’re a microenterprise), although many small businesses still make a conscientious decision to comply and pursue greater usability and long-term competitiveness.
3. Integrate accessibility into development
The important thing to know about the EAA and related standards is that businesses not only must meet accessibility requirements once, but the principles of accessibility need to be embedded into your design, development, and content creation workflows instead of being added as an afterthought.
This involves:
- Designing with accessibility in mind (including color contrast, font size, clear navigation)
- Using semantic HTML and ARIA labels
- Ensuring mobile responsiveness
- Writing content that is readable and understandable by all
Work with developers, designers, content creators, and QA teams within the process from the start. Accessibility-by-design is both more efficient and more cost-effective than introducing fixes later.
4. Test regularly for accessibility
Similarly to developing products with accessibility in mind, accessibility testing should be ongoing, not a one-off effort. This helps prevent common accessibility errors from making their way into the finished solution. Use a mix of:
- Automated testing to quickly catch common errors
- Manual testing to evaluate user experience and compliance nuances
- Assistive technology testing, such as screen readers and keyboard-only navigation
- Real-user testing with people who have disabilities (this is optional but highly valuable)
Regular testing ensures compliance isn’t lost during updates or redesigns and that accessibility becomes a sustained practice.
5. Document and communicate accessibility
Compliance also requires clear documentation and transparency, which are among the most important accessibility best practices. To ensure clear and concise documentation, businesses should:
- Publish accessibility statements in line with EAA expectations
- Keep records of testing and remediation efforts
- Provide customer support that is accessible and available in multiple channels (live chat, voice, or text relay)
- Offer product guides, contracts, and terms in formats usable by people with disabilities
Good documentation shows regulators you’re taking compliance seriously, as well as helps build trust with users who rely on accessible solutions.
EAA Checklist: A Structured Approach to Compliance
Whether you’re only starting your process of becoming EAA-compliant or you are running an accessibility audit to make sure you don’t miss anything, keeping up with all the requirements for European Accessibility Act can prove to be surprisingly challenging. If you’re worried about missing something important, we’ve got you covered! A free EAA compliance checklist will help you remain on track with your accessibility efforts and streamline the processes to stay ahead of the stricter rules.
Best Practices for the European Accessibility Act Compliance
Meeting the basic requirements of the European Accessibility Act is essential, but to create truly inclusive digital experiences and further propel your business to success, it’s a good idea to go further. Beyond the core obligations, there are several practical steps that can strengthen your compliance posture, improve usability, and reduce legal risk. These best practices help embed accessibility into your operations, ensuring that your digital services are not only compliant but also genuinely inclusive for all users.
1. Train your staff on accessibility principles
Accessibility isn’t the responsibility of a single team. Designers, developers, content writers, QA engineers, and support agents should all receive regular training. Educating your staff helps prevent accessibility issues from the start and fosters a culture of inclusion across your organization.
2. Support keyboard and gesture-based navigation
Users must be able to interact with your services without relying on a mouse or touchpad. Ensure all functionality can be accessed via a keyboard alone. For mobile and touch interfaces, support common gestures and ensure they work well with voice commands or screen readers.
3. Ensure accessible authentication and security processes
Authentication methods like CAPTCHAs, biometrics, and two-factor authentication should be usable by people with various impairments. Avoid relying solely on visual or auditory cues. Provide accessible alternatives, such as audio CAPTCHAs or one-time codes via SMS or email.
4. Make emergency services accessible
If your product or service involves access to emergency communication (such as telecoms or in-vehicle systems), ensure users with disabilities can send real-time text, share location data, and receive emergency alerts in accessible formats.
5. Enable user personalization features
Support options like adjustable font sizes, high contrast modes, and simplified layouts. Letting users tailor their experience improves usability and expands access to people with low vision, dyslexia, or cognitive disabilities.
6. Test for compatibility with assistive technologies beyond screen readers
Screen readers are important, but they’re not the only assistive technology users rely on. Make sure your systems also work with screen magnifiers, switch devices, voice input, and alternative keyboards to support a broader user base.
7. Offer a clear accessibility feedback mechanism
Allow users to report accessibility issues easily through a dedicated form, email address, or contact point. This shows your commitment to inclusion and helps identify and fix problems faster, before they become compliance risks.
Let Us Help You Spot and Fix Accessibility Issues
Whether you are just starting your journey to full accessibility or simply aren’t sure where your risks lie, TestFort can support you at every stage of the process. Our team provides thorough accessibility audits based on standards like WCAG 2.1 and EN 301 549, combining automated tools with manual testing to catch real-world usability barriers that prevent you from being EAA-compliant and serving your customers better. We evaluate websites, apps, documents, and digital interfaces to identify where you fall short of EAA requirements and offer practical recommendations for remediation.
Beyond testing, we work closely with your design, development, and content teams to help implement accessibility from the ground up. Whether it’s redesigning key user flows, fixing code-level issues, or improving compatibility with assistive technologies, we focus on long-term improvements, not just temporary fixes. You don’t need to figure it out alone — we’re here to make accessibility manageable, measurable, and compliant.
Is Your Product EAA-Ready?
We will help you know for sure.
Final Thoughts
Accessibility may seem complex, especially when new regulations like the European Accessibility Act come into play. But ultimately, it’s about enabling more people to access and benefit from what you offer. That way, you can expand your reach and seamlessly expand to foreign markets without leaving behind an important group of users with disabilities. For businesses, this isn’t just a compliance task — it’s an opportunity to gain wider audiences, improve user experience, and build digital products that truly work for everyone. If you’ve been thinking about becoming compliant for a while, this is the sign that you need to start soon!
Jump to section
- What Is the European Accessibility Act?
- European Accessibility Act 2025 Deadline
- Businesses, Products and Services That EAA Applies To
- Who Can Be Exempt From Being Compliant?
- What Happens If You Don’t Ensure Compliance With the EAA?
- Why Else EAA Compliance Matters
- Key Requirements of the EU Accessibility Act
- How to Comply With the EAA: The 5-Step Process
- EAA Checklist: A Structured Approach to Compliance
- Best Practices for the European Accessibility Act Compliance
- 1. Train your staff on accessibility principles
- 2. Support keyboard and gesture-based navigation
- 3. Ensure accessible authentication and security processes
- 4. Make emergency services accessible
- 5. Enable user personalization features
- 6. Test for compatibility with assistive technologies beyond screen readers
- 7. Offer a clear accessibility feedback mechanism
- Let Us Help You Spot and Fix Accessibility Issues
- Final Thoughts
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!