Though the Internet of Things (IoT) has redefined our lives and brought a lot of benefits, it has a large attack surface area that’s highly vulnerable to cyber attacks. If not properly secured, IoT devices can be easily hacked by cybercriminals, which can lead to serious consequences, especially in niches like finance that deals with lots of financial and sensitive customer data. Therefore, the Internet of Things solutions require much more thorough testing to prevent information leaks and damage to the hardware. How to do it right, what types of IoT testing exist, and which techniques are the most effective – keep reading to find answers to all of these questions.
Key Takeaways
- The rapid expansion of IoT devices increases the risk of cyberattacks, making robust security measures essential.
- Weak passwords, insecure network services, outdated components, and poor device management are some of the most common vulnerabilities in IoT ecosystems.
- IoT devices are frequently targeted by various cyberattacks, including DDoS, ransomware, MitM, brute force, and phishing attacks. The more interconnected devices become, the larger the attack surface for cybercriminals.
- To prevent cyber security attacks and protect IoT systems, comprehensive testing, including penetration testing, threat modeling, and firmware analysis, is essential.
- Implementing security measures such as segmentation, network security, regular software updates, and integrating teams from the design stage can significantly reduce IoT vulnerabilities.
The Importance of Securing Your IoT
The IoT market is growing quickly. Perhaps there’s no area that smart devices haven’t touched. From healthcare to everyday life, IoT devices have become our reliable assistants, just a step behind smartphones in their ubiquity. As we look at the statistics, we can see they will gain even more traction in the coming years. Predictions show that the number of devices could reach 29 billion by 2030 — double the 15.1 billion recorded in 2020. These numbers reveal that IoT will continue to be a lucrative industry that will keep growing.
However, the downside is that this industry is highly susceptible to attacks. If not properly secured, IoT devices can become a gateway for cybercriminals, allowing them to access sensitive data and tamper with systems. This vulnerability is not just a threat to individual privacy but also poses potential security risks to businesses and national security.
You might have heard of some really bad attacks that have occurred because of unsecured IoT devices. One of the most sensational cases, without a doubt, is the Mirai botnet attack in 2016. In just one day, millions of IoT devices were hijacked to launch a massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, disrupting Internet services across the globe. This security incident alone is enough to illustrate the catastrophic consequences of neglecting IoT security.
What Is IoT Security Testing?
Considering the risks of focusing too much on the usability of devices and ignoring their security, IoT security testing becomes a critical component in safeguarding the entire IoT ecosystem. Essentially, Internet of Things security testing is what it says on the tin. It’s the practice of evaluating cloud-connected devices and networks to reveal security flaws and prevent devices from being hacked and compromised by a third party. The biggest IoT security risks and challenges can be addressed through comprehensive testing strategies and a focused approach to the most critical IoT vulnerabilities.
Most Critical IoT Security Vulnerabilities
There are typical issues in security analysis faced by organizations that need to be addressed, even by experienced companies. Consequently, adequate testing of Internet of Things security in networks and devices is required, as a single security breach in the system can bring a business to a standstill, leading to financial losses and declining customer loyalty.
Let’s take a closer look at the most malicious security issues to watch out for.
Weak Easy-to-Guess Passwords
Absurdly simple and short passwords that put personal data at risk are among the primary IoT security risks and vulnerabilities for most cloud-connected devices and their owners. Hackers can co-opt multiple devices with a single guessable password, jeopardizing the entire IoT network.
Insecure Ecosystem Interfaces
Insufficient encryption and verification of the user’s identity or access rights in the ecosystem architecture (i.e., software, hardware, firmware, network, and interfaces outside of the device) enable the devices and associated components to get infected by malware. Any element in the broad network of connected technologies is a potential source of risk.
Insecure Network Services
Particular attention should be paid to services running on the device, especially those exposed to the Internet and with a high risk of unauthorized access. Do not keep ports open, update protocols, and ban any unusual traffic.
Outdated Components
Outdated software components or frameworks leave connected devices vulnerable to cyberattacks. These security weaknesses allow third parties to access the internal network and tamper with the performance of these gadgets, potentially operating them remotely or expanding the attack surface for the organization.
Insecure Data Transfer/ Storage
The more devices connected to the Internet, the higher the data storage/exchange level must be. Failure to securely encode sensitive data, whether stored or transmitted, can cause the entire system to fail.
Bad IoT Device Management
Inadequate management of IoT devices occurs due to poor network perception and visibility. Organizations may have many different devices that they do not even know about and that provide easy entry points for attackers. IoT developers are simply not prepared in terms of proper planning, implementation, and management tools.
Poor Secure Update Mechanism
The ability to securely update the software, which is the core of any IoT device, reduces the chances of it being compromised. The gadget becomes vulnerable every time cybercriminals discover a weak point in security. Similarly, if it is not fixed with regular updates, or if there are no regular notifications of security-related changes, it can become compromised over time.
Inadequate Privacy Protection
Personal information is gathered and stored in larger amounts on IoT devices than smartphones. In case of improper access, there is always a threat of your information being exposed and exploited for malicious purposes. It is a major privacy concern because most Internet of Things technologies, to some extent, are related to monitoring and controlling gadgets at home, which can lead to serious consequences later on.
Poor Physical Hardening
Poor physical hardening is another critical vulnerability. These devices are often placed in easily accessible locations like offices and public places, making them prone to physical tampering. Without robust physical security measures, attackers can gain access to these devices, allowing them to manipulate, extract, or destroy data. This vulnerability is particularly concerning for devices used in critical infrastructure.
Insecure Default Settings
Some IoT devices come with default settings that cannot be modified, or operators need alternatives regarding security adjustments. The initial configuration should be adjustable. Default settings that are invariant across multiple devices are insecure. Once guessed, they can be used to hack into other devices.
Bring in external expertise.
Our team can help you create a reliable and safe IoT product
While the number of IoT devices grows, so does the number of cyber security attacks. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities, and IoT devices have become their prime targets. However, knowing the types of threats that exist can make your life a lot easier and help you take the necessary precautions to protect your IoT devices. Here are the most common types of cyber security attacks:
Types of Cyber Security Attacks on IoT Devices
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
One of the most common threats to IoT devices is the DDoS attack. In these attacks, cybercriminals infect multiple devices with malware to create a botnet. This botnet, controlled by cybercriminals, then floods a target (often a server) with an overwhelming amount of traffic, causing it to crash. IoT devices are particularly vulnerable because they are often left unsecured, making them easy to hijack.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks
In a Man-in-the-Middle attack, an attacker intercepts the communication between two devices. For IoT devices, which frequently transmit sensitive data, this can lead to significant breaches of privacy. Attackers can eavesdrop on conversations, manipulate transmitted data, or even hijack the connection entirely.
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks have made headlines in recent years, and IoT devices are not immune. Just in 2023, the number of IoT attacks increased by 400%, and it’s clear that attackers aren’t going to stop there. In these attacks, hackers gain control of an IoT device and lock the owner out, demanding a ransom to regain access. This can be particularly dangerous in cases where the IoT device controls critical infrastructure, such as smart home systems, healthcare systems, or industrial machinery.
Firmware attacks
Many IoT devices run on outdated or unpatched firmware, making them vulnerable to attacks. Cybercriminals exploit these weaknesses to inject malicious code into the device’s firmware, which can lead to data theft, device malfunction, or even the spread of malware to other connected devices.
Brute Force attacks
Another type of malware in IoT is a brute force attack. This type of attack is performed to steal a device’s password by trying multiple combinations until the right one is found. Brute Force attacks are used not only on IoT devices, but since IoT devices typically have rather weak default passwords, they become a particularly attractive target for attackers. When hackers gain access to a device, they can use it as part of a large botnet.
Phishing attacks
IoT devices are also susceptible to phishing attacks – a type of attack that tricks users into revealing their sensitive data, such as login and passwords and financial details. Phishing attacks typically use fraudulent emails or messages, or even phone calls, and since the source they come from usually looks legitimate, many people fall for the trap, making this a rather alarming threat.
Side-Channel Attacks
Side-channel attacks are a type of attack that exploits the physical properties of IoT devices, such as its power consumption, electromagnetic emissions, or even sound. These attacks allow hackers to retrieve sensitive information like encryption keys and other confidential data from IoT devices without direct intervention into the software or hardware. While these attacks are less common than DDoS and MitM, they pose a real threat to IoT devices from critical industries, such as government, healthcare, and finance.
AI-based attacks
AI attacks aren’t something new; in fact, its brain power has been used by intruders for more than 10 years, in particular for abuse on social media websites. However, in recent years, the popularity of AI-based attacks has grown exponentially. Moreover, many of the AI tools designed for hacks have become accessible for buy, making them available to pretty much anyone.
As you can guess, this is just a glimpse of the many possible attacks targeting IoT devices. The more advanced our gadgets become, the more appealing they are to cybercriminals, and the more new types of malware emerge to exploit their vulnerabilities.
Generally speaking, any organization or individual using IoT devices could be at risk of a cyber security attack. However, industries like finance, healthcare, government, and manufacturing are particularly vulnerable due to the critical nature of the data and operations involved. This makes it essential for them to invest in thorough security testing to prevent potentially devastating consequences.
Internet of Things Attack Surface Areas
By and large, there are three types of surface areas in IoT systems that are particularly vulnerable to attacks. These include:
- Devices – intruders often initiate attacks on the device’s components such as memory, firmware, web interface, and network services. They may tamper with the gadget’s settings, exploit outdated components, or inject malicious code into the vulnerable firmware. In some cases, they may manipulate sensors, ports, and other hardware components, disrupting the entire system and causing significant malfunctions.
- Communication channels – Attacks can get through communication channels connecting IoT devices. Protocols, which act as the backbone of IoT systems, are particularly vulnerable. If affected by malicious firmware, they may impact the whole IoT framework. Furthermore, communication channels are highly susceptible to DoS and spoofing attacks, which can lead to the disruption of services and unauthorized access.
- Software and applications – Imperfections in the frameworks of IoT applications and software can lead to severe vulnerabilities. Weaknesses in software design, outdated libraries, or flawed application logic may serve as entry points for attackers. Once breached, cybercriminals can exploit these vulnerabilities to steal user credentials, run unsafe updates, or deploy malicious payloads.
AI-Enhanced Testing for Creative Console Systems
How an Attack Occurs
When a cyberattack targets the device or the software, it typically follows a sequence of steps that allows the hacker to infiltrate the device and accomplish their malicious goals. Here’s what usually happens:
Initial access
The attacker begins by scanning the organization’s network with specialized tools to locate vulnerable devices that have open ports. Once found, they capture the device’s IP address, marking the entry point for their attack.
Infiltration
After finding an unprotected device, the attacker may use various methods to inject malicious code. This command forces the device’s operating system to download and execute malware, which allows the attacker to proceed with harmful activities.
Persistence
The deployed malware embeds itself within the device, ensuring long-term control. It modifies the system to disable monitoring tools and creates new user accounts to maintain access. By keeping the device’s system shell open, the attacker establishes a persistent backdoor for future entry.
Evasion techniques
To avoid being detected, hackers use evasion strategies. These may include deleting system logs and command history, hiding malicious files behind seemingly innocent names, and disabling the device’s security tools. Oftentimes, they also employ anti-debugging and anti-virtualization techniques, helping them to further conceal their presence.
Data harvesting
At this point, the attacker begins collecting all available data from the compromised device, which could include encryption keys, financial data, or cryptocurrency wallets. In more advanced attacks, the intruder may infect network devices such as switches or storage systems, gathering confidential data from network traffic.
Command and Control
Following instructions from a command-and-control (C&C) server, the malware continues to carry out destructive tasks. For example, it may launch network-based attacks like TCP or UDP flooding, or even spread the infection to additional devices. The C&C communication channels can vary, using protocols such as HTTP, IRC, or peer-to-peer (P2P) networks.
Lateral movement
Once cybercriminals have control over the initial device, they may laterally move within the network searching for other vulnerable systems. For example, if they compromised a gateway router, the next step could be infiltrating IoT devices connected to it. This way, the attack would spread further across the entire network.
Final impact
The consequences of these attacks can be severe. From encrypting data for ransom to wiping the entire drives and rendering the device completely inoperable without the option to recover, the damage can be catastrophic. Worse still, the impact can extend beyond the device itself. If the IoT device is part of a critical infrastructure, the attack can lead to widespread service disruptions.
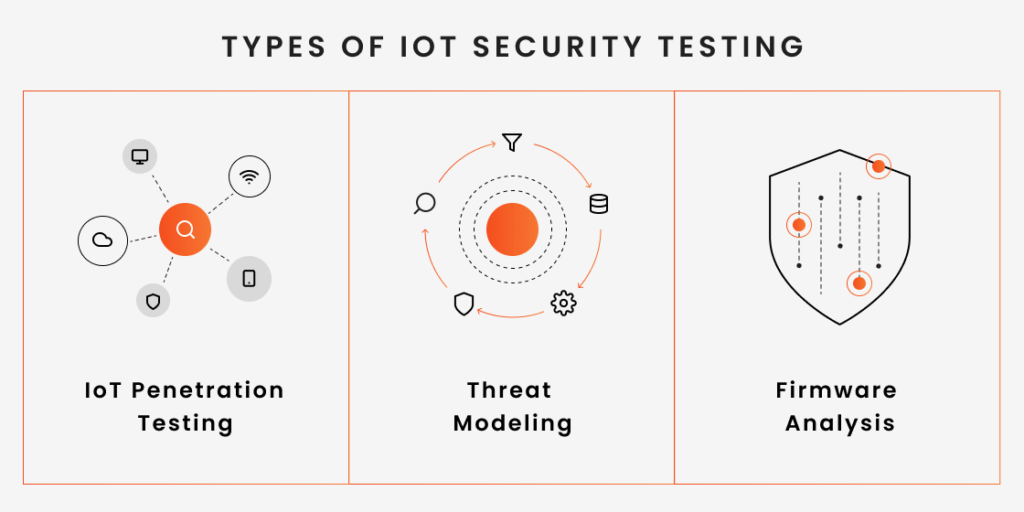
Types of IoT Security Testing
Now that we’ve covered the most common security vulnerabilities and the types of possible attacks, it’s time to learn about IoT security testing methods to help identify and mitigate these risks. Each type of testing aims at targeting different aspects of IoT security to keep systems safe.
IoT Penetration Testing
IoT penetration testing is a simulated attack performed by security teams to identify vulnerabilities in devices and enhance data security. IoT penetration testers conduct real-world evaluations of the entire IoT system, which includes not just the device and the software product but the whole connected ecosystem.
Threat Modeling
Another popular method used to find security issues in IoT devices or networks is threat modeling. In this testing activity, security professionals create a checklist of the most probable attack methods and suggest countermeasures to mitigate them. This method aims at ensuring the security of systems by providing an analysis of necessary security controls.
Firmware Analysis
Firmware analysis is an essential part of IoT security testing. This process delves deep into the firmware, the core software embedded directly in the hardware of IoT products, such as routers, heart monitors, and so on. By examining the firmware, security testers can identify vulnerabilities like backdoors and buffer overflows that might not be apparent on the surface but could have significant implications for the overall security program of an IoT device.
Best Practices to Protect IoT Systems and Devices
Gadgets offering great UX but lacking data privacy can pose significant risks to IoT systems and devices. To mitigate these risks and enhance security, adopting a set of security best practices is crucial. Here are some key strategies that can help you ensure the security of your IoT devices:
- Introduce IoT security during the design phase. IoT security strategy is most valuable if initially introduced during the design stage. Most concerns and threats with risks to an Internet of Things solution may be avoided by identifying them during preparation and planning.
- Network security. Since networks pose the risk of any IoT device being remotely controlled, they play a critical role in cyber protection strategy. The network stability is ensured by port security, antimalware, firewalls, and banned IP addresses a user does not usually use.
- API security. Sophisticated businesses and websites use APIs to connect services, transfer data, and integrate various types of information in one place, making them a target for hackers. A hacked API can result in the disclosure of confidential information. That is why only approved apps and devices should be permitted to send requests and responses with APIs.
- Segmentation. Following segmentation for a corporate network is essential if multiple IoT devices connect directly to the web. Each device should use its small local network (segment) with limited access to the main network.
- Security gateways. They serve as an additional level in security IoT infrastructure before sending data a device produces to the Internet. They help to track and analyze incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring someone else cannot directly reach the gadget.
- Software updates. Users should be able to set changes to software and devices by updating them over a network connection or through automation. Improved software means incorporating new features and assisting in identifying and eliminating security defects in the early stages.
- Integrating teams. Many people are involved in the IoT development process. They are equally responsible for ensuring the product’s security throughout the full lifecycle. It is preferable to have IoT developers get together with security experts to share guidance and necessary security controls right from the design stage.
To create trustworthy devices and protect them from cyber threats, you have to maintain a defensive and proactive security strategy throughout the entire development cycle.
Best Tools for IoT Pentesting
As we’ve mentioned, performing Internet of Things security testing requires a set of solid skills and in-depth knowledge of various domains. On top of that, it’s vital to be adept at using IoT pentesting tools. Let’s briefly outline what types of pentesting tools exist and which of them deserve the attention of security professionals.

Types of IoT pentesting tools
Any security professional and pentester should have extensive knowledge and hands-on experience using various IoT penetration testing tools. These tools can be grouped into several categories such as:
- Port scanners – as the name suggests, these tools help discover open ports on the system. Using these tools, testers can see which of the applications are currently running on a network and protect them from malicious hackers’ attacks.
- Vulnerability scanners – these tools help identify vulnerabilities within an IoT system, device, or network. By scanning for known security weaknesses, they allow pentesters to pinpoint areas that may be susceptible to attacks. Vulnerability scanning is a critical step in IoT penetration testing, where devices often have various embedded systems that can be prone to security flaws.
- Network sniffers – these tools provide testers with the ability to check what’s happening with network traffic, where the traffic comes from, and what protocols and parts are used. As a rule, network sniffers are used to see if data is encrypted and what communication paths are vulnerable to unsafe activities.
- Web proxies – these are essential tools in IoT security assessment as they allow testers to intercept and analyze communication between a device and external systems. By acting as an intermediary, web proxies can help identify insecure data transmissions, weak authentication mechanisms, or improper handling of sensitive information.
- Password crackers – these tools are crucial in IoT devices security testing. Many IoT devices rely on simple, default, or weak passwords, which can be easily exploited by attackers. Password cracking tools allow testers to test the strength of passwords used in IoT devices by attempting to crack them and implement stronger security practices.
Now, let’s delve into the tools that shine the spotlight in the field of IoT security and should be mastered by security professionals.
- Wireshark: This tool is essential for network protocol analysis and packet capture. It helps in understanding the data flow and spotting vulnerabilities in network communications.
- NMAP: A network scanning tool, Nmap is crucial for discovering devices on a network, identifying open ports, and detecting services running on IoT devices.
- Metasploit: This framework is key for developing and executing exploit code against a remote target machine. It’s widely used for vulnerability validation and demonstrating the impact of vulnerabilities.
- Burp Suite: An integrated platform for performing security testing of web applications, Burp Suite is invaluable for testing IoT devices that interact with web-based interfaces.
- Aircrack-Ng: For IoT systems that use wireless communication, Aircrack-ng is a must-have for assessing network security and performing tasks like network monitoring and traffic analysis.
- John the Ripper: As a password-cracking tool, John the Ripper is widely used for recovering passwords and testing the strength of password security in IoT devices.
- SQLMap: This tool automates detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws, which is crucial for testing IoT devices that interact with databases.
- OWASP ZAP: An open-source tool for finding vulnerabilities in web applications, OWASP ZAP is particularly useful for testing IoT devices with web interfaces.
- Binwalk: Specializing in firmware analysis, Binwalk is used for extracting and analyzing the firmware of IoT devices, which is essential for understanding device operation and potential vulnerabilities.
Each of these tools helps with IoT security assessment, offering insights into the potential risks that may interfere with a connected device, and is a must-have in the toolkit of any penetration tester and security professional. However, be advised that the list of IoT application security testing tools expands all the time, making it important to stay on top of the latest developments in security tools and practices.
QA Audit and Process Optimization for Drone Software
The Benefits of Hiring Professional Security Teams
Unless you have in-house expertise, hiring a professional team of testers specializing in IoT security testing is a wise decision. Testing IoT systems is a complex task. It encompasses a variety of domains, including cloud-based services, mobile, web, hardware, and firmware. These areas can easily divert your focus from core business operations and potentially hinder your growth. Therefore, bringing in expertise from the outside can be a strategic move.
At QArea, we’ve got a wealth of experience in evaluating the security of diverse IoT ecosystems. From identifying vulnerabilities in cloud-based services to identifying the intricacies of mobile, web, hardware, and firmware components, we are adept at the best testing practices and can guarantee our clients strong protection against potential threats.
Here’s just a small part of what our team can do for you:
Review Your IoT Security Architecture
Our team will thoroughly review your IoT security architecture, identifying any vulnerabilities in IoT devices. We’ll assess the robustness of your application security and ensure that your IoT devices’ security and privacy aspects are up to standard. This review is crucial in understanding how well your devices and their software can withstand potential security threats.
Perform Penetration Testing
We specialize in penetration testing. By simulating real-world attacks, we can identify weaknesses in your system before malicious actors try to exploit them. This includes testing both the hardware and software components of your IoT ecosystem.
Test the Entire IoT Ecosystem
Our approach is holistic; we test the entire ecosystem. This means not just looking at individual devices but also how they interact within the network. Monitoring IoT devices in their operational environment allows us to provide comprehensive security solutions.
Conduct All Types of Security Testing
We conduct all types of security testing, from static and dynamic analysis to software composition analysis. This ensures that every aspect of your IoT system, from the device firmware to the software development lifecycle, is secure and resilient against cyber threats.
Assess Risks
Risk assessment is a key part of our service. We evaluate the potential risks associated with your IoT devices and systems, providing you with a clear understanding of where your vulnerabilities lie and how they can impact your business.
Ensure Compliance
Finally, we ensure that your IoT systems comply with the latest industry standards and regulations. This step is vital in safeguarding against scenarios where your software security is compromised. By adhering to these standards, we help maintain the trust of your customers and protect your organization from potential legal and financial repercussions.
Bottom Line
The importance of IoT cannot be overstated. The Internet of Things is rising today, and many businesses are actively implementing it. However, such massive dependence on a vast network of devices for personal and professional use raises the need for rigorous security testing. Only by closing security gaps and staying on guard of the safety and privacy of networks can we truly take advantage of these advanced technologies and smartly interact with the modern world.
Jump to section
- Key Takeaways
- The Importance of Securing Your IoT
- What Is IoT Security Testing?
- Types of Cyber Security Attacks on IoT Devices
- Internet of Things Attack Surface Areas
- How an Attack Occurs
- Types of IoT Security Testing
- Best Practices to Protect IoT Systems and Devices
- Best Tools for IoT Pentesting
- The Benefits of Hiring Professional Security Teams
- Bottom Line
Hand over your project to the pros.
Let’s talk about how we can give your project the push it needs to succeed!